Non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) uptake by T lymphocytes: evidence for the selective acquisition of oligomeric ferric citrate species
- PMID: 24278199
- PMCID: PMC3836815
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079870
Non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) uptake by T lymphocytes: evidence for the selective acquisition of oligomeric ferric citrate species
Abstract
Iron is an essential nutrient in several biological processes such as oxygen transport, DNA replication and erythropoiesis. Plasma iron normally circulates bound to transferrin. In iron overload disorders, however, iron concentrations exceed transferrin binding capacity and iron appears complexed with low molecular weight molecules, known as non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI). NTBI is responsible for the toxicity associated with iron-overload pathologies but the mechanisms leading to NTBI uptake are not fully understood. Here we show for the first time that T lymphocytes are able to take up and accumulate NTBI in a manner that resembles that of hepatocytes. Moreover, we show that both hepatocytes and T lymphocytes take up the oligomeric Fe3Cit3 preferentially to other iron-citrate species, suggesting the existence of a selective NTBI carrier. These results provide a tool for the identification of the still elusive ferric-citrate cellular carrier and may also open a new pathway towards the design of more efficient iron chelators for the treatment of iron overload disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





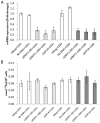


References
-
- Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU, Galy B, Camaschella C (2010) Two to tango: regulation of Mammalian iron metabolism. Cell 142: 24–38. - PubMed
-
- Breuer W, Hershko C, Cabantchik ZI (2000) The importance of non-transferrin bound iron in disorders of iron metabolism. Transfus Sci 23: 185–192. - PubMed
-
- Esposito BP, Breuer W, Sirankapracha P, Pootrakul P, Hershko C, et al. (2003) Labile plasma iron in iron overload: redox activity and susceptibility to chelation. Blood 102: 2670–2677. - PubMed
-
- Zimelman AP, Zimmerman HJ, McLean R, Weintraub LR (1977) Effect of iron saturation of transferrin on hepatic iron uptake: an in vitro study. Gastroenterology 72: 129–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

