Plasma interferon-gamma-inducible protein-10 levels are associated with early, but not sustained virological response during treatment of acute or early chronic HCV infection
- PMID: 24278230
- PMCID: PMC3835825
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080003
Plasma interferon-gamma-inducible protein-10 levels are associated with early, but not sustained virological response during treatment of acute or early chronic HCV infection
Abstract
Background: High plasma levels of interferon-gamma inducible protein-10 (IP-10) have been shown to be associated with impaired treatment response in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Whether IP-10 levels predict treatment in acute HCV infection is unknown.
Methods: Patients with acute or early chronic HCV infection from the Australian Trial in Acute Hepatitis C (ATAHC) cohort were evaluated. Baseline and on-treatment plasma IP-10 levels were measured by ELISA. IL28B genotype was determined by sequencing.
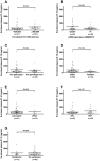
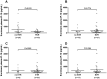
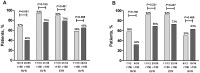
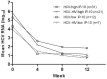
Results: Overall, 74 HCV mono-infected and 35 HIV/HCV co-infected patients were treated in ATAHC, of whom 89 were adherent to therapy and were included for analysis. IP-10 levels correlated with HCV RNA levels at baseline (r = 0.48, P<0.001) and during treatment. Baseline IP-10 levels were higher in patients who failed to achieve rapid virological response (RVR). Only one patient with a plasma IP-10 level >600 pg/mL achieved RVR. There was no association with IP-10 levels and early virological response (EVR) or sustained virological response (SVR).
Conclusions: Baseline IP-10 levels are associated with early viral kinetics but not ultimate treatment outcome in acute HCV infection. Given previous data showing that patients with high baseline IP-10 are unlikely to spontaneously clear acute HCV infection, they should be prioritized for early antiviral therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Grebely J, Matthews GV, Dore GJ (2011) Treatment of acute HCV infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8: 265–274. - PubMed
-
- Jaeckel E, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H, Santantonio T, Mayer J, et al. (2001) Treatment of acute hepatitis C with interferon alfa-2b. N Engl J Med 345: 1452–1457. - PubMed
-
- Wiegand J, Deterding K, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H (2008) Treatment of acute hepatitis C: the success of monotherapy with (pegylated) interferon alpha. J Antimicrob Chemother 62: 860–865. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Borozan I, Feld J, Sun J, Tannis LL, et al. (2005) Hepatic gene expression discriminates responders and nonresponders in treatment of chronic hepatitis C viral infection. Gastroenterology 128: 1437–1444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

