Non-invasive in vivo imaging of near infrared-labeled transferrin in breast cancer cells and tumors using fluorescence lifetime FRET
- PMID: 24278268
- PMCID: PMC3836976
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080269
Non-invasive in vivo imaging of near infrared-labeled transferrin in breast cancer cells and tumors using fluorescence lifetime FRET
Abstract
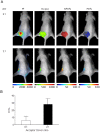
The conjugation of anti-cancer drugs to endogenous ligands has proven to be an effective strategy to enhance their pharmacological selectivity and delivery towards neoplasic tissues. Since cell proliferation has a strong requirement for iron, cancer cells express high levels of transferrin receptors (TfnR), making its ligand, transferrin (Tfn), of great interest as a delivery agent for therapeutics. However, a critical gap exists in the ability to non-invasively determine whether drugs conjugated to Tfn are internalized into target cells in vivo. Due to the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, it remains unknown whether these Tfn-conjugated drugs are specifically internalized into cancer cells or are localized non-specifically as a result of a generalized accumulation of macromolecules near tumors. By exploiting the dimeric nature of the TfnR that binds two molecules of Tfn in close proximity, we utilized a Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) based technique that can discriminate bound and internalized Tfn from free, soluble Tfn. In order to non-invasively visualize intracellular amounts of Tfn in tumors through live animal tissues, we developed a novel near infrared (NIR) fluorescence lifetime FRET imaging technique that uses an active wide-field time gated illumination platform. In summary, we report that the NIR fluorescence lifetime FRET technique is capable of non-invasively detecting bound and internalized forms of Tfn in cancer cells and tumors within a live small animal model, and that our results are quantitatively consistent when compared to well-established intensity-based FRET microscopy methods used in in vitro experiments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Barbet J, Bardies M, Bourgeois M, Chatal JF, Cherel M, et al. (2012) Radiolabeled antibodies for cancer imaging and therapy. Methods Mol Biol 907: 681–697. - PubMed
-
- Dijkers EC, Kosterink JG, Rademaker AP, Perk LR, van Dongen GA, et al. (2009) Development and characterization of clinical-grade 89Zr-trastuzumab for HER2/neu immunoPET imaging. J Nucl Med 50: 974–981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

