Cyanide poisoning deaths detected at the national forensic service headquarters in seoul of Korea: a six year survey (2005~2010)
- PMID: 24278610
- PMCID: PMC3834424
- DOI: 10.5487/TR.2012.28.3.195
Cyanide poisoning deaths detected at the national forensic service headquarters in seoul of Korea: a six year survey (2005~2010)
Abstract
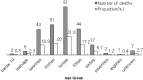
The records of 255 cyanide poisoning deaths obtained from National Forensic Service (NFS) headquarters, located in Seoul of Korea, from 2005 to 2010 were retrospectively reviewed. The mean age was 41.88 ± 13.09 and range was 6~80 years (unknown in seven cases). The number of deaths of males and females were 200 and 53, respectively (unknown in two cases). The largest number of cases occurred in people aged 40-49 years (81 cases, 31.8%), followed by the age groups 30~39 years (51 cases, 20%), 50~59 years (44 cases, 17.2%) and 20~29 years (43 cases, 16.9%). The total number of deaths among other age groups (below 10, 10~19, 60~69, 70~79, over 80 years and unknown) were 36, representing only 14.1%. Of all cyanide poisoning deaths, 97.3% were due to suicide, and 14.5% of the total number who died received medical treatment. The most frequent site for ingestion was the person's own residence (120 cases, 47.1%) and the route of administration was mainly oral (252, 98.8%). From the total of 255 cyanide poisoning cases, white powders were submitted for analysis in 92 cases. Potassium cyanide and sodium cyanide occupied 51 and 41 cases, respectively. This study showed that poisoning deaths due to cyanide are one of the continuously reported public health problems in Korea. Enforcement of regulations and safety education to prevent cyanide poisoning should be carried out by the government.
Keywords: Cyanide; Poisoning; Suicide.
Figures
References
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Cyanide. Dep. Health Human Services; Atlanta, United States: (2006). pp. 1–341. - PubMed
-
- Baselt R.C. Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. 8th edition. Biomedical Publications; California: (2008). pp. 373–377.
-
- Dalpe-Scott M., Degouffe M., Garbutt D., Drost M. A comparison of drug concentration in postmortem cardiac and peripheral blood in 320 cases. Canadian Soc. Forens. Sci. J. (1995);28:113–121.
-
- Gil J.R., Marker E., Staji M. Suicide by cyanide: 17 deaths. J. Forens. Sci. (2004);49:826–828. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources