Involvement of inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice depressive-like behaviors
- PMID: 24279434
- PMCID: PMC6493120
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12170
Involvement of inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice depressive-like behaviors
Abstract
Aims: The NLRP3 inflammasome is a cytoplasmic multiprotein complex of the innate immune system that regulates the cleavage of interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 precursors. It can detect a wide range of danger signals and trigger a series of immune-inflammatory reactions. There were plenty of studies indicating that activation of the immune system played pivotal roles in depression. However, the underlying mechanisms of immune-depression interactions remained elusive and there was no report about the involvement of inflammasome activation in depression.
Methods: We established an acute depression mouse model with lipopolysaccharide to explore the involvement of inflammasome activation in depression.
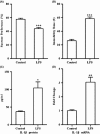
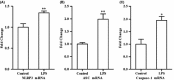
Results: The lipopolysaccharide-treated mice displayed depressive-like behaviors and pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β protein and mRNA levels significantly increased. The NLRP3 inflammasome mRNA expression level also significantly elevated in depressed mice brain. Pretreatment with the NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CMK significantly abrogated the depressive-like behaviors induced by lipopolysaccharide.
Conclusion: These data suggest for the first time that the NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice depressive-like behaviors. The NLRP3 inflammasome may be a central mediator between immune activation and depression, which raises the possibility that it may be a more specific target for the depression treatments in the near future.
Keywords: Cytokines; Depression; Inflammation; Interleukin-1β; NLRP3 inflammasome.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . The global burden of disease: 2004 update, Vol. 4. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2008;39–51.
-
- Dunn AJ, Swiergiel AH, de Beaurepaire R. Cytokines as mediators of depression: What can we learn from animal studies? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2005;29:891–909. - PubMed
-
- Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ben‐Menachem‐Zidon O, et al. Brain interleukin‐1 mediates chronic stress‐induced depression in mice via adrenocortical activation and hippocampal neurogenesis suppression. Mol Psychiatry 2008;13:717–728. - PubMed
-
- Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010;140:821–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

