Prostanoid receptor EP2 as a therapeutic target
- PMID: 24279689
- PMCID: PMC4045661
- DOI: 10.1021/jm401431x
Prostanoid receptor EP2 as a therapeutic target
Abstract
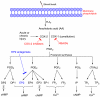
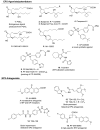
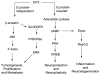
Cycoloxygenase-2 (COX-2) induction is prevalent in a variety of (brain and peripheral) injury models where COX-2 levels correlate with disease progression. Thus, COX-2 has been widely explored for anti-inflammatory therapy with COX-2 inhibitors, which proved to be effective in reducing the pain and inflammation in patients with arthritis and menstrual cramps, but they have not provided any benefit to patients with chronic inflammatory neurodegenerative disease. Recently, two COX-2 drugs, rofecoxib and valdecoxib, were withdrawn from the United States market due to cardiovascular side effects. Thus, future anti-inflammatory therapy could be targeted through a specific prostanoid receptor downstream of COX-2. The PGE2 receptor EP2 is emerging as a pro-inflammatory target in a variety of CNS and peripheral diseases. Here we highlight the latest developments on the role of EP2 in diseases, mechanism of activation, and small molecule discovery targeted either to enhance or to block the function of this receptor.
Figures




References
-
- Minghetti L. Role of inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2005;18:315–321. - PubMed
-
- Baumgart DC, Carding SR. Gastroenterology 1 - Inflammatory bowel disease: cause and immunobiology. Lancet. 2007;369:1627–1640. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:2205–2219. - PubMed
-
- Sethi S, Mahler DA, Marcus P, Owen CA, Yawn B, Rennard S. Inflammation in COPD: implications for management. Am. J. Med. 2012;125:1162–1170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

