Risk for transmission of Naegleria fowleri from solid organ transplantation
- PMID: 24279908
- PMCID: PMC4676565
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12536
Risk for transmission of Naegleria fowleri from solid organ transplantation
Abstract
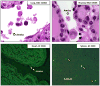
Primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) caused by the free-living ameba (FLA) Naegleria fowleri is a rare but rapidly fatal disease of the central nervous system (CNS) affecting predominantly young, previously healthy persons. No effective chemotherapeutic prophylaxis or treatment has been identified. Recently, three transplant-associated clusters of encephalitis caused by another FLA, Balamuthia mandrillaris, have occurred, prompting questions regarding the suitability of extra-CNS solid organ transplantation from donors with PAM. During 1995-2012, 21 transplant recipients of solid organs donated by five patients with fatal cases of PAM were reported in the United States. None of the recipients developed PAM, and several recipients tested negative for N. fowleri by serology. However, historical PAM case reports and animal experiments with N. fowleri, combined with new postmortem findings from four patients with PAM, suggest that extra-CNS dissemination of N. fowleri can occur and might pose a risk for disease transmission via transplantation. The risks of transplantation with an organ possibly harboring N. fowleri should be carefully weighed for each individual recipient against the potentially greater risk of delaying transplantation while waiting for another suitable organ. In this article, we present a case series and review existing data to inform such risk assessments.
Keywords: Ameba; Naegleria; amoeba; disseminated; primary amebic meningoencephalitis; transplant.
© Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Yoder JS, Straif-Bourgeois S, Roy SL, Moore TA, Visvesvara GS, Ratard RC, Hill VR, Wilson JD, Linscott AJ, Crager R, Kozak NA, Sriram R, Narayanan J, Mull B, Kahler AM, Schneeberger C, da Silva AJ, Poudel M, Baumgarten KL, Xiao L, Beach MJ. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis deaths associated with sinus irrigation using contaminated tap water. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55:e79–85. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoder JS, Eddy BA, Visvesvara GS, Capewell L, Beach MJ. The epidemiology of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in the USA, 1962–2008. Epidemiol Infect. 2010;138:968–975. - PubMed
-
- Seidel JS, Harmatz P, Visvesvara GS, Cohen A, Edwards J, Turner J. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:346–348. - PubMed
-
- Vargas-Zepeda J, Gómez-Alcalá AV, Vázquez-Morales JA, Licea-Amaya L, De Jonckheere JF, Lares-Villa F. Successful treatment of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis by using intravenous amphotericin B, fluconazole, and rifampicin. Arch Med Res. 2005;36:83–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

