Heritable alteration in salt-tolerance in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia)
- PMID: 24280025
- PMCID: PMC4883729
- DOI: 10.1186/1939-8433-5-36
Heritable alteration in salt-tolerance in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia)
Abstract
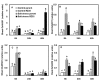
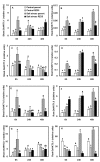
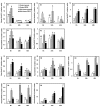
Background: Introgression as a means of generating phenotypic novelty, including altered stress tolerance, is increasingly being recognized as common. The underlying basis for de novo genesis of phenotypic variation in the introgression lines remains largely unexplored. In this investigation, we used a rice line (RZ35) derived from introgressive hybridization between rice (Oryza sativa L.) and wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.), along with its rice parental line (cv. Matsumae) as the experimental materials. We compared effects of salt stress on growth, ion homeostasis, and relevant gene expression between RZ35 and Matsumae, to explore possible mechanisms of heritable alteration in stress tolerance induced by the introgression.
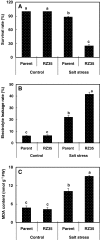
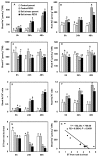
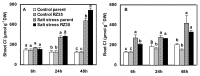
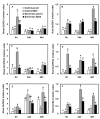
Results: Contrary to our expectation, the results showed that the inhibitory effect of salt stress on growth of RZ35 was significantly greater than that of Matsumae. We further found that a major underlying cause for this outcome is that the introgression process weakened the capacity in Na+ exclusion under the salt stress condition, and hence, escalated the injuries of Na+ and Cl- in shoots of RZ35. Accordingly, based on q-RT-PCR analysis, four genes known to be involved in the Na+ exclusion, i.e., OsHKT1;5, OsSOS1, OsCIPK24 and OsCBL4, were found to be significantly down-regulated in roots of RZ35 relative to its rice parental line under the salt stress condition, thus implicating a gene expression regulation-based molecular mechanism underlying the difference in salt stress-tolerance between the introgression line and its rice parental line.
Conclusions: We show that introgression represents a potent means for rapidly generating de novo heritable variations in physiological traits like stress tolerance in plants, although the direction of the alteration appears unpredictable.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomewide variation in an introgression line of rice-Zizania revealed by whole-genome re-sequencing.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 18;8(9):e74479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074479. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24058573 Free PMC article.
-
Transpositional reactivation of the Dart transposon family in rice lines derived from introgressive hybridization with Zizania latifolia.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Aug 26;10:190. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-190. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20796287 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive microsatellite variation in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.).PLoS One. 2013 Apr 24;8(4):e62317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062317. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23638037 Free PMC article.
-
Extent and pattern of DNA methylation alteration in rice lines derived from introgressive hybridization of rice and Zizania latifolia Griseb.Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Jul;113(2):196-205. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0286-2. Epub 2006 May 5. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16791687
-
Extensive de Novo genomic variation in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.).Genetics. 2005 Aug;170(4):1945-56. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.040964. Epub 2005 Jun 3. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15937131 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
2,4-D attenuates salinity-induced toxicity by mediating anatomical changes, antioxidant capacity and cation transporters in the roots of rice cultivars.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 5;7(1):10443. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09708-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28874677 Free PMC article.
-
Back to the Wild: On a Quest for Donors Toward Salinity Tolerant Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Mar 20;11:323. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00323. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32265970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple cold resistance loci confer the high cold tolerance adaptation of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon) to its high-latitude habitat.Theor Appl Genet. 2015 Jul;128(7):1359-71. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2511-3. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Theor Appl Genet. 2015. PMID: 25862679
-
Advances in Sensing, Response and Regulation Mechanism of Salt Tolerance in Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 24;22(5):2254. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052254. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of QTLs Regulating Six Agronomic Traits of Rice Based on Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines of Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) and Mapping of qPH1.1 and qLMC6.1.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 11;12(12):1850. doi: 10.3390/biom12121850. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedinia M, Henry RJ, Blakeney AB, Lewin LG. Accessing genes in the tertiary gene pool of rice by direct introduction of total DNA from Zizania palustris (wild rice) Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2000;18:133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF02824021. - DOI
-
- Ainouche ML, Baumel A, Salmon A, Yannic G. Hybridization, polyploidy and speciation in Spartina (Poaceae) New Phytol. 2004;161:165–172. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00926.x. - DOI
-
- Amrutha RN, Sekhar PN, Varshney RK, Kishor P. Genome-wide analysis and identification of genes related to potassium transporter families in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant Sci. 2007;172:708–721. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.11.019. - DOI
-
- Ashraf M. Some important physiological selection criteria for salt tolerance in plants. Flora. 2004;199:361–376. doi: 10.1078/0367-2530-00165. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

