Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross (MAGIC) populations in rice: progress and potential for genetics research and breeding
- PMID: 24280183
- PMCID: PMC4883706
- DOI: 10.1186/1939-8433-6-11
Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross (MAGIC) populations in rice: progress and potential for genetics research and breeding
Abstract
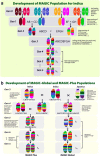
Background: This article describes the development of Multi-parent Advanced Generation Inter-Cross populations (MAGIC) in rice and discusses potential applications for mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) and for rice varietal development. We have developed 4 multi-parent populations: indica MAGIC (8 indica parents); MAGIC plus (8 indica parents with two additional rounds of 8-way F1 inter-crossing); japonica MAGIC (8 japonica parents); and Global MAGIC (16 parents - 8 indica and 8 japonica). The parents used in creating these populations are improved varieties with desirable traits for biotic and abiotic stress tolerance, yield, and grain quality. The purpose is to fine map QTLs for multiple traits and to directly and indirectly use the highly recombined lines in breeding programs. These MAGIC populations provide a useful germplasm resource with diverse allelic combinations to be exploited by the rice community.
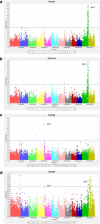
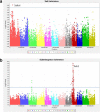
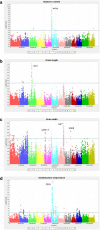
Results: The indica MAGIC population is the most advanced of the MAGIC populations developed thus far and comprises 1328 lines produced by single seed descent (SSD). At the S4 stage of SSD a subset (200 lines) of this population was genotyped using a genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach and was phenotyped for multiple traits, including: blast and bacterial blight resistance, salinity and submergence tolerance, and grain quality. Genome-wide association mapping identified several known major genes and QTLs including Sub1 associated with submergence tolerance and Xa4 and xa5 associated with resistance to bacterial blight. Moreover, the genome-wide association study (GWAS) results also identified potentially novel loci associated with essential traits for rice improvement.
Conclusion: The MAGIC populations serve a dual purpose: permanent mapping populations for precise QTL mapping and for direct and indirect use in variety development. Unlike a set of naturally diverse germplasm, this population is tailor-made for breeders with a combination of useful traits derived from multiple elite breeding lines. The MAGIC populations also present opportunities for studying the interactions of genome introgressions and chromosomal recombination.
Figures


References
-
- AACC . Approved Methods of the AACC. 61–03. 9. St. Paul, MN, USA: American Association of Cereal Chemists; 1999. p. 4.
-
- Alam R, Sazzadur Rahman M, Seraj ZI. Investigation of seedling-stage salinity tolerance QTLs using backcross lines derived from Oryza sativa L. Pokkali. Plant Breeding. 2011;130:430–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0523.2010.01837.x. - DOI
-
- Allard R. Breeding methods with self pollinated crops. New York: Principles of Breeding. John Wiley and Sons. Inc.; 1960.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

