LKB1 is a central regulator of tumor initiation and pro-growth metabolism in ErbB2-mediated breast cancer
- PMID: 24280377
- PMCID: PMC4178213
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-3002-1-18
LKB1 is a central regulator of tumor initiation and pro-growth metabolism in ErbB2-mediated breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Germline and somatic mutations in STK11, the gene encoding the serine/threonine kinase LKB1, are strongly associated with tumorigenesis. While loss of LKB1 expression has been linked to breast cancer, the mechanistic role of LKB1 in regulating breast cancer development, metastasis, and tumor metabolism has remained unclear.
Methods: We have generated and analyzed transgenic mice expressing ErbB2 in the mammary epithelium of LKB1 wild-type or LKB1-deficient mice. We have also utilized ErbB2-expressing breast cancer cells in which LKB1 levels have been reduced using shRNA approaches. These transgenic and xenograft models were characterized for the effects of LKB1 loss on tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and tumor cell metabolism.
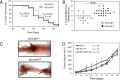
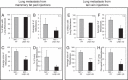
Results: We demonstrate that loss of LKB1 promotes tumor initiation and induces a characteristic shift to aerobic glycolysis ('Warburg effect') in a model of ErbB2-mediated breast cancer. LKB1-deficient breast cancer cells display enhanced early tumor growth coupled with increased cell migratory and invasive properties in vitro. We show that ErbB2-positive tumors deficient for LKB1 display a pro-growth molecular and phenotypic signature characterized by elevated Akt/mTOR signaling, increased glycolytic metabolism, as well as increased bioenergetic markers both in vitro and in vivo. We also demonstrate that mTOR contributes to the metabolic reprogramming of LKB1-deficient breast cancer, and is required to drive glycolytic metabolism in these tumors; however, LKB1-deficient breast cancer cells display reduced metabolic flexibility and increased apoptosis in response to metabolic perturbations.
Conclusions: Together, our data suggest that LKB1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. Loss of LKB1 collaborates with activated ErbB2 signaling to drive breast tumorigenesis and pro-growth metabolism in the resulting tumors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Loss of LKB1 expression reduces the latency of ErbB2-mediated mammary gland tumorigenesis, promoting changes in metabolic pathways.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056567. Epub 2013 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451056 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the tumor suppressor LKB1 promotes metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells via HIF-1α.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):2554-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312570111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550282 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical study of drug combinations that reduce breast cancer burden due to aberrant mTOR and metabolism promoted by LKB1 loss.Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 30;5(24):12738-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2818. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25436981 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1 deficiency-induced metabolic reprogramming in tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic diseases.Mol Metab. 2021 Feb;44:101131. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101131. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33278637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tumor Suppressor Kinase LKB1: Metabolic Nexus.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 28;10:881297. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.881297. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573694 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Relevance of Liver Kinase B1(LKB1) Protein and Gene Expression in Breast Cancer.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 15;6:21374. doi: 10.1038/srep21374. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26877155 Free PMC article.
-
Pyruvate kinase M knockdown-induced signaling via AMP-activated protein kinase promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, autophagy, and cancer cell survival.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 15;292(37):15561-15576. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.791343. Epub 2017 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28778925 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2015 Dec;12(4):342-54. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2015.0089. Cancer Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26779371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin Antagonizes Cancer Cell Proliferation by Suppressing Mitochondrial-Dependent Biosynthesis.PLoS Biol. 2015 Dec 1;13(12):e1002309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002309. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 26625127 Free PMC article.
-
The double-edged sword of AMPK signaling in cancer and its therapeutic implications.Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Mar;38(3):346-57. doi: 10.1007/s12272-015-0549-z. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Arch Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25575627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hemminki A, Markie D, Tomlinson I, Avizienyte E, Roth S, Loukola A, Bignell G, Warren W, Aminoff M, Höglund P, Järvinen H, Kristo P, Pelin K, Ridanpää M, Salovaara R, Toro T, Bodmer W, Olschwang S, Olsen AS, Stratton MR, de la Chapelle A, Aaltonen LA. A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature. 1998;391(6663):184–187. doi: 10.1038/34432. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hearle N, Schumacher V, Menko FH, Olschwang S, Boardman LA, Gille JJ, Keller JJ, Westerman AM, Scott RJ, Lim W, Trimbath JD, Giardiello FM, Gruber SB, Offerhaus GJ, de Rooij FW, Wilson JH, Hansmann A, Möslein G, Royer-Pokora B, Vogel T, Phillips RK, Spigelman AD, Houlston RS. Frequency and spectrum of cancers in the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. ClinCancer Res. 2006;12(10):3209–3215. - PubMed
-
- Partanen JI, Tervonen TA, Myllynen M, Lind E, Imai M, Katajisto P, Dijkgraaf GJ, Kovanen PE, Mäkelä TP, Werb Z, Klefström J. Tumor suppressor function of Liver kinase B1 (Lkb1) is linked to regulation of epithelial integrity. ProcNatlAcadSci USA. 2012;109(7):388–397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120421109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

