Characterization of the human ESC transcriptome by hybrid sequencing
- PMID: 24282307
- PMCID: PMC3864310
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1320101110
Characterization of the human ESC transcriptome by hybrid sequencing
Abstract
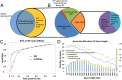
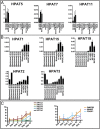
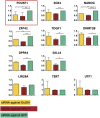
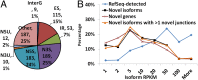
Although transcriptional and posttranscriptional events are detected in RNA-Seq data from second-generation sequencing, full-length mRNA isoforms are not captured. On the other hand, third-generation sequencing, which yields much longer reads, has current limitations of lower raw accuracy and throughput. Here, we combine second-generation sequencing and third-generation sequencing with a custom-designed method for isoform identification and quantification to generate a high-confidence isoform dataset for human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). We report 8,084 RefSeq-annotated isoforms detected as full-length and an additional 5,459 isoforms predicted through statistical inference. Over one-third of these are novel isoforms, including 273 RNAs from gene loci that have not previously been identified. Further characterization of the novel loci indicates that a subset is expressed in pluripotent cells but not in diverse fetal and adult tissues; moreover, their reduced expression perturbs the network of pluripotency-associated genes. Results suggest that gene identification, even in well-characterized human cell lines and tissues, is likely far from complete.
Keywords: PacBio; alternative splicing; hESC transcriptome; isoform discovery; lncNRA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


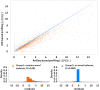
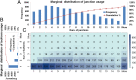

References
-
- Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5(7):621–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

