Diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis
- PMID: 24282356
- PMCID: PMC3837265
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7661
Diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis
Abstract
IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is often associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. However, the diffuse cholangiographic abnormalities observed in IgG4-SC may resemble those observed in primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and the presence of segmental stenosis suggests cholangiocarcinoma (CC). IgG4-SC responds well to steroid therapy, whereas PSC is only effectively treated with liver transplantation and CC requires surgical intervention. Since IgG4-SC was first described, it has become a third distinct clinical entity of sclerosing cholangitis. The aim of this review was to introduce the diagnostic methods for IgG4-SC. IgG4-SC should be carefully diagnosed based on a combination of characteristic clinical, serological, morphological, and histopathological features after cholangiographic classification and targeting of a disease for differential diagnosis. When intrapancreatic stenosis is detected, pancreatic cancer or CC should be ruled out. If multiple intrahepatic stenoses are evident, PSC should be distinguished on the basis of cholangiographic findings and liver biopsy with IgG4 immunostaining. Associated inflammatory bowel disease is suggestive of PSC. If stenosis is demonstrated in the hepatic hilar region, CC should be discriminated by ultrasonography, intraductal ultrasonography, bile duct biopsy, and a higher cutoff serum IgG4 level of 182 mg/dL.
Keywords: IgG4; IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis; Primary sclerosing cholangitis; Sclerosing cholangitis.
Figures


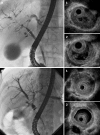
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic procedures for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011 Mar;18(2):127-36. doi: 10.1007/s00534-010-0320-2. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011. PMID: 20814701 Review.
-
Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis based on cholangiographic classification.J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jan;47(1):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0465-z. Epub 2011 Sep 23. J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 21947649
-
IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis.Semin Liver Dis. 2016 Aug;36(3):216-28. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1584321. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Semin Liver Dis. 2016. PMID: 27466792 Review.
-
Clinical clues to suspicion of IgG4-associated sclerosing cholangitis disguised as primary sclerosing cholangitis or hilar cholangiocarcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Dec;25(12):1831-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06411.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 21091993
-
Isolated intrapancreatic IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 28;21(4):1334-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1334. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25632210 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Secondary sclerosing cholangitis and IgG4-sclerosing cholangitis - A review of cholangiographic and ultrasound imaging.Endosc Ultrasound. 2023 Mar-Apr;12(2):181-199. doi: 10.4103/EUS-D-22-00208. Endosc Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 36588352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Involving the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts Diagnosed with Liver Biopsy.Case Rep Pathol. 2018 Sep 16;2018:2309293. doi: 10.1155/2018/2309293. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30305974 Free PMC article.
-
Two cases of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis in which transabdominal ultrasonography was useful in diagnosis and follow-up observation.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2016 Apr;43(2):271-7. doi: 10.1007/s10396-015-0676-7. Epub 2015 Oct 14. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2016. PMID: 27033871
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis in the context of IgG4-related disease: review of imaging findings.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15177-89. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15177. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Hepatopancreaticobiliary diseases in IgG4-associated autoimmune diseases].Radiologe. 2016 Dec;56(12):1052-1060. doi: 10.1007/s00117-016-0185-8. Radiologe. 2016. PMID: 27853829 Review. German.
References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Sato Y, Tsuneyama K, Haratake J, Kurumaya H, Katayanagi K, Masuda S, Niwa H, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:1193–1203. - PubMed
-
- Naitoh I, Nakazawa T, Ohara H, Ando T, Hayashi K, Tanaka H, Okumura F, Takahashi S, Joh T. Endoscopic transpapillary intraductal ultrasonography and biopsy in the diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:1147–1155. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Egawa N, Nakajima H. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–984. - PubMed
-
- Ohara H, Nakazawa T, Sano H, Ando T, Okamoto T, Takada H, Hayashi K, Kitajima Y, Nakao H, Joh T. Systemic extrapancreatic lesions associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2005;31:232–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

