Dendritic cell co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory markers in chronic HCV: an Egyptian study
- PMID: 24282359
- PMCID: PMC3837270
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7711
Dendritic cell co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory markers in chronic HCV: an Egyptian study
Abstract
Aim: To assess co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory markers of dendritic cells (DCs) in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infected subjects with and without uremia.
Methods: Three subject groups were included in the study: group 1 involved 50 control subjects, group 2 involved 50 patients with chronic HCV infection and group 3 involved 50 HCV uremic subjects undergoing hemodialysis. CD83, CD86 and CD40 as co-stimulatory markers and PD-L1 as a co-inhibitory marker were assessed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Interleukin-10 (IL-10) and hyaluronic acid (HA) levels were also assessed. All findings were correlated with disease activity, viral load and fibrogenesis.
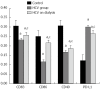
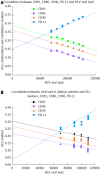
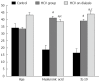
Results: There was a significant decrease in co-stimulatory markers; CD83, CD86 and CD40 in groups 2 and 3 vs the control group. Co-stimulatory markers were significantly higher in group 3 vs group 2. There was a significant elevation in PD-L1 in both HCV groups vs the control group. PD-L1 was significantly lower in group 3 vs group 2. There was a significant elevation in IL-10 and HA levels in groups 2 and 3, where IL-10 was higher in group 3 and HA was lower in group 3 vs group 2. HA level was significantly correlated with disease activity and fibrosis grade in group 2. IL-10 was significantly correlated with fibrosis grade in group 2. There were significant negative correlations between co-stimulatory markers and viral load in groups 2 and 3, except CD83 in dialysis patients. There was a significant positive correlation between PD-L1 and viral load in both HCV groups.
Conclusion: A significant decrease in DC co-stimulatory markers and a significant increase in a DC co-inhibitory marker were observed in HCV subjects and to a lesser extent in dialysis patients.
Keywords: CD83; CD86, CD40; Dendritic cells; Hemodialysis; Hepatitis C virus; Hyaluronic acid; Interleukin-10; PD-L1; Uremia.
Figures

References
-
- Guerra J, Garenne M, Mohamed MK, Fontanet A. HCV burden of infection in Egypt: results from a nationwide survey. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19:560–567. - PubMed
-
- Sievert W, Altraif I, Razavi HA, Abdo A, Ahmed EA, Alomair A, Amarapurkar D, Chen CH, Dou X, El Khayat H, et al. A systematic review of hepatitis C virus epidemiology in Asia, Australia and Egypt. Liver Int. 2011;31 Suppl 2:61–80. - PubMed
-
- Khodir SA, Alghateb M, Okasha KM, Shalaby Sel-S. Prevalence of HCV infections among hemodialysis patients in Al Gharbiyah Governorate, Egypt. Arab J Nephrol Transplant. 2012;5:145–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

