Supernumerary kidney laparoscopically treated
- PMID: 24282475
- PMCID: PMC3840517
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.788
Supernumerary kidney laparoscopically treated
Abstract
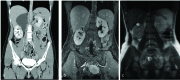
Congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract are part of a family of diseases with different anatomical origins. Duplicated collecting systems can be defined as a renal unit containing 2 pyelocalyceal systems associated with a single ureter or with double ureters. The supernumerary kidney is a definitive accessory organ with its own collecting system, blood supply, and distinct encapsulated parenchima. The true incidence of supernumerary kidney remains unknown, but most cases are in males, are unilateral and on the left side. We present a case of an adult woman with a hypoplastic supernumerary kidney with a complete ureteral duplication and an ectopic junction. The case has been laparoscopically treated. We demonstrate that a laparoscopic nephro-ureterectomy is feasible and that the management of the complication (urinoma and fistula) can be managed conservatively.
Figures

References
-
- Schlussel RN, Retik AB. Ectopic ureter, ureterocele, and other anomalies of the ureter. In: Walsh PC, editor. Campbell’s Urology. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2002. pp. 2007–52.
-
- Oto A, Kerimoglu U, Eskicorapci S, et al. Bilateral supernumerary kidney: Imaging findings. JBR-BTR. 2002;85:300–3. - PubMed
-
- Bernik TR, Ravnic DJ, Bernik SF, et al. Ectopic supernumerary kidney, a cause of para-aortic mass: Case report and review. Am Surg. 2001;67:657–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
