The coronary slow flow phenomenon: characteristics, mechanisms and implications
- PMID: 24282683
- PMCID: PMC3839135
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-3652.2011.10.01
The coronary slow flow phenomenon: characteristics, mechanisms and implications
Abstract
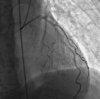
The coronary slow flow phenomenon (CSFP) is an important, angiographic entity characterized by delayed progression of the injected contrast medium through the coronary tree. It is a frequent finding, typically observed in patients presenting with acute coronary syndromes. Although it is well known to interventional cardiologists for approximately four decades, the pathogenic mechanisms remain unclear. The clinical implications are significant, with over 80% of patients experiencing recurrent chest pain, resulting in considerable impairment in quality of life. This article will address in detail the characteristics, possible mechanisms, and clinical implications of this entity to provide further insight into its clinical significance and management strategies.
Keywords: chest pain; coronary slow flow phenomenon; coronary tree.
Figures


References
-
- Cutri N, Zeitz C, Kucia AM, et al. ST/T wave changes during acute coronary syndrome presentation in patients with the coronary slow flow phenomenon. Int J Cardiol 2011;146:457-8. - PubMed
-
- Horjeti B, Goda A. Acute ischemia manifestation in a patient with coronary slow flow phenomenon. J Electrocardiol 2012;45:277-9. - PubMed
-
- Wozakowska-Kapłon B, Niedziela J, Krzyzak P, et al. Clinical manifestations of slow coronary flow from acute coronary syndrome to serious arrhythmias. Cardiol J 2009;16:462-8. - PubMed
-
- Tambe AA, Demany MA, Zimmerman HA, et al. Angina pectoris and slow flow velocity of dye in coronary arteries--a new angiographic finding. Am Heart J 1972;84:66-71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
