Human acellular dermal wound matrix: evidence and experience
- PMID: 24283346
- PMCID: PMC7950764
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12185
Human acellular dermal wound matrix: evidence and experience
Abstract
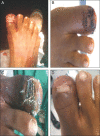
A chronic wound fails to complete an orderly and timely reparative process and places patients at increased risk for wound complications that negatively impact quality of life and require greater health care expenditure. The role of extracellular matrix (ECM) is critical in normal and chronic wound repair. Not only is ECM the largest component of the dermal skin layer, but also ECM proteins provide structure and cell signalling that are necessary for successful tissue repair. Chronic wounds are characterised by their inflammatory and proteolytic environment, which degrades the ECM. Human acellular dermal matrices, which provide an ECM scaffold, therefore, are being used to treat chronic wounds. The ideal human acellular dermal wound matrix (HADWM) would support regenerative healing, providing a structure that could be repopulated by the body's cells. Experienced wound care investigators and clinicians discussed the function of ECM, the evidence related to a specific HADWM (Graftjacket(®) regenerative tissue matrix, Wright Medical Technology, Inc., licensed by KCI USA, Inc., San Antonio, TX), and their clinical experience with this scaffold. This article distills these discussions into an evidence-based and practical overview for treating chronic lower extremity wounds with this HADWM.
Keywords: ECM; Extracellular matrix; Graftjacket RTM; Human acellular dermal matrix; Regenerative tissue matrix.
© 2013 The Authors. International Wound Journal © 2013 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of a human acellular dermal wound matrix in patients with complex wounds and comorbidities.J Wound Care. 2015 Jun;24(6):261-2, 264-7. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.6.261. J Wound Care. 2015. PMID: 26075374
-
Human acellular dermal wound matrix for treatment of DFU: literature review and analysis.J Wound Care. 2015 Mar;24(3):128; 129-34. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.3.128. J Wound Care. 2015. PMID: 25764957 Review.
-
Use of an acellular regenerative tissue matrix over chronic wounds.Eplasty. 2013 Nov 20;13:e61. eCollection 2013. Eplasty. 2013. PMID: 24324850 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Cellular and Acellular Matrix Products: Indications, Techniques, and Outcomes.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016 Sep;138(3 Suppl):138S-147S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002643. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016. PMID: 27556754 Review.
-
[Influence of porcine urinary bladder matrix and porcine acellular dermal matrix on wound healing of full-thickness skin defect in diabetic mice].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 20;36(12):1130-1138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200901-00399. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33379849 Chinese.
Cited by
-
A prospective, randomised, controlled, multicentre clinical trial examining healing rates, safety and cost to closure of an acellular reticular allogenic human dermis versus standard of care in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers.Int Wound J. 2017 Apr;14(2):307-315. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12600. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Int Wound J. 2017. PMID: 27073000 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Deep burn surgery of the whole dorsum of the hand: Composite skin grafting over acellular dermal matrix versus thick split-thickness skin grafting.Int Wound J. 2024 May;21(5):e14934. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14934. Int Wound J. 2024. PMID: 38783559 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Factor-Reinforced ECM Fabricated from Chemically Hypoxic MSC Sheet with Improved In Vivo Wound Repair Activity.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2578017. doi: 10.1155/2017/2578017. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29018809 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical fragility of outcomes in acellular dermal matrix literature: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2024 Apr;91:284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2024.02.047. Epub 2024 Feb 11. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2024. PMID: 38432086 Free PMC article.
-
A long-term follow-up study of diabetic foot ulcer using micronized acellular dermal matrix.Int Wound J. 2023 May;20(5):1622-1637. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14018. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Int Wound J. 2023. PMID: 36377547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bornstein P, Sage EH. Matricellular proteins: extracellular modulators of cell function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2002;14:608–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

