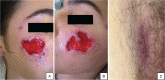
Facial superficial granulomatous pyoderma
- PMID: 24283375
- PMCID: PMC7950330
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12195
Facial superficial granulomatous pyoderma
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyoderma gangrenosum in the head and neck.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007 Jan;133(1):83-5. doi: 10.1001/archotol.133.1.83. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007. PMID: 17224531 No abstract available.
-
Facial pyoderma gangrenosum triggered by leishmaniasis in a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022 Feb;47(2):444-445. doi: 10.1111/ced.14938. Epub 2021 Oct 10. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34554592 No abstract available.
-
Superficial granulomatous pyoderma treated with intravenous immunoglobulin.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Mar;48(3):456-60. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.172. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12637931
-
Superficial granulomatous pyoderma: a case in an 11-year-old girl and review of the literature.Pediatr Dermatol. 2010 Sep-Oct;27(5):496-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01271.x. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 21182640 Review.
-
Pyoderma gangrenosum.Clin Dermatol. 2000 May-Jun;18(3):283-93. doi: 10.1016/s0738-081x(99)00119-4. Clin Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 10856660 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A Case of Overlapping Clinical Features of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis, Hidradenitis Suppurativa, and Pyoderma Gangrenosum Successfully Treated with Adalimumab.Case Rep Dermatol. 2022 May 3;14(2):98-106. doi: 10.1159/000523801. eCollection 2022 May-Aug. Case Rep Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35702373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Winkelmann RK, Wilson‐Jones E, Gibson LE, Quimby SR. Histopathologic features of superficial granulomatous pyoderma. J Dermatol 1989;16:127–32. - PubMed
-
- Quimby S, Gibson L, Winkelmann R. Superficial granulomatous pyoderma: clinicopathologic spectrum. Mayo Clin Proc 1989;64:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Hardwick N, Cerio R. Superficial granulomatous pyoderma: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol 1993;129:718–22. - PubMed
-
- Thami G, Kaur S, Punia R, Kanwart A. Superficial granulomatous pyoderma: an idiopathic granulomatous cutaneous ulceration. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2002;16:159–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources