The effect of relaxin on the musculoskeletal system
- PMID: 24283470
- PMCID: PMC4282454
- DOI: 10.1111/sms.12149
The effect of relaxin on the musculoskeletal system
Abstract
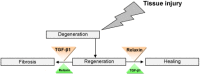
Relaxin is a hormone structurally related to insulin and insulin-like growth factor, which exerts its regulatory effect on the musculoskeletal and other systems through binding to its receptor in various tissues, mediated by different signaling pathways. Relaxin alters the properties of cartilage and tendon by activating collagenase. This hormone is also involved in bone remodeling and healing of injured ligaments and skeletal muscle. In this review, we have summarized the literature on the effect of relaxin in musculoskeletal system to provide a broad perspective for future studies in this field.
Keywords: ligament; motor organs; relaxin; skeletal muscle; tendon.
© 2013 The Authors. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Albert H, Godskesen M, Westergaard JG, Chard T, Gunn L. Circulating levels of relaxin are normal in pregnant women with pelvic pain. Eur J Obstet Gyn R B. 1997;74(1):19–22. - PubMed
-
- Arnold C, Van Bell C, Rogers V, Cooney T. The relationship between serum relaxin and knee joint laxity in female athletes. Orthopedics. 2002;25(6):669–673. - PubMed
-
- Bani D, Nistri S, Cinci L, Giannini L, Princivalle M, Elliott L, Bigazzi M, Masini E. A novel, simple bioactivity assay for relaxin based on inhibition of platelet aggregation. Regul Pept. 2007;144(1–3):10–16. - PubMed
-
- Bathgate RAD, Halls ML, Van Der Westhuizen ET, Callander GE, Kocan M, Summers RJ. Relaxin family peptides and their receptors. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(1):405–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

