Development of an air-stable nickel precatalyst for the amination of aryl chlorides, sulfamates, mesylates, and triflates
- PMID: 24283652
- PMCID: PMC3926134
- DOI: 10.1021/ol403209k
Development of an air-stable nickel precatalyst for the amination of aryl chlorides, sulfamates, mesylates, and triflates
Abstract
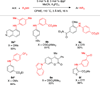
A new air-stable nickel precatalyst for C-N cross-coupling is reported. The developed catalyst system displays a greatly improved substrate scope for C-N bond formation to include both a wide range of aryl and heteroaryl electrophiles and aryl, heteroaryl, and alkylamines. The catalyst system is also compatible with a weak base, allowing the amination of substrates containing base-sensitive functional groups.
Figures




References
-
- Wolfe JP, Buchwald SL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997;119:6054.
-
- Bolm C, Hildebrand JP, Rudolph J. Synthesis. 2000;7:911.
- Tobisu M, Shimasaki T, Chatani N. Chem. Lett. 2009;38:710.
- Shimasaki T, Tobisu M, Chatani N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010;49:2929. - PubMed
- Ackermann L, Sandmann R, Song W. Org. Lett. 2011;13:1784. - PubMed
- Ackermann L, Song W, Sandmann R. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011;696:195.
- Mesganaw T, Silberstein AL, Ramgren SD, Nathel NFF, Hong X, Liu P, Garg NK. Chem. Sci. 2011;2:1766. - PMC - PubMed
- Ramgren SD, Silberstein AL, Yang Y, Garg NK. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011;50:2171. - PMC - PubMed
- Tobisu M, Yasutome A, Yamakawa K, Shimasaki T, Chatani N. Tetrahedron. 2012;68:5157.
-
- Miller J, Dankwardt J, Penney J. Synthesis. 2003:1643.
-
- Brenner E, Fort Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:5359.
- Brenner E, Schneider R, Fort Y. Tetrahedron. 1999;55:12829.
- Brenner E, Schneider R, Fort Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000;41:2881.
- Lipshutz BH, Ueda H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000;39:4492. - PubMed
- Gradel B, Brenner E, Schneider R, Fort Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001;42:5689.
- Desmarets C, Schneider Rl, Fort Y. J. Org. Chem. 2002;67:3029. - PubMed
- Omar-Amrani R, Thomas A, Brenner E, Schneider R, Fort Y. Org. Lett. 2003;5:2311. - PubMed
- Chen C, Yang L-M. Org. Lett. 2005;7:2209. - PubMed
- Manolikakes G, Gavryushin A, Knochel P. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:1429. - PubMed
- Gao C-Y, Cao X, Yang L-M. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009;7:3922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

