Lack of in vitro effect of aglepristone on IFN-γ and IL-4 production by resting and mitogen-activated T cells of luteal bitches
- PMID: 24284004
- PMCID: PMC3818567
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-220
Lack of in vitro effect of aglepristone on IFN-γ and IL-4 production by resting and mitogen-activated T cells of luteal bitches
Abstract
Background: Aglepristone (RU534) is an antiprogestin used for pregnancy termination, parturition induction and conservative pyometra treatment in bitches. Its molecular structure is similar to mifepristone, an antiprogestin used in human medicine. Mifepristone has been shown to suppress proliferation and cytokine production by T cells, whereas the effect of aglepristone on T cell function remains elusive. The purpose of this project was to investigate the in vitro influence of RU534 on IFN-γ and IL-4 synthesis by peripheral blood T cells isolated from healthy bitches (N = 16) in luteal phase. The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were incubated with three different dosages of aglepristone, or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), with or without mitogen. The production of cytokines by resting or mitogen-activated T cells was determined by intercellular staining and flow cytometry analysis or ELISA assay, respectively.
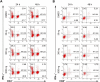
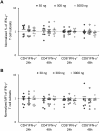
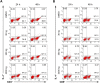
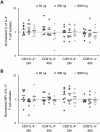
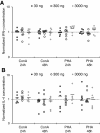
Results: Our results showed no statistically significant differences in the percentage of IFN-γ and IL-4-synthesizing CD4+ or CD8+ resting T cells between untreated and aglepristone-treated cells at 24 and 48 hours post treatment. Moreover, mitogen-activated PBMCs treated with RU534 displayed similar concentration of IFN-γ and IL-4 in culture supernatants to those observed in mitogen-activated DMSO-treated PBMCs. Presented results indicate that administration of aglepristone for 48 hours has no influence on IFN-γ and IL-4 synthesis by resting and mitogen-activated T cells isolated from diestral bitches.
Conclusions: We conclude that antiprogestins may differentially affect T cell function depending on the animal species in which they are applied.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokine production by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in mice following primary exposure to chemical allergens: evidence for functional differentiation of T lymphocytes in vivo.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1998 Jun;116(2):116-23. doi: 10.1159/000023934. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9652304
-
Influence of longterm therapy with methotrexate and low dose corticosteroids on type 1 and type 2 cytokine production in CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2001 Aug;28(8):1793-9. J Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11508581 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of cocaine administration to influenza virus-immunized mice on cytokine profiles of individual splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Dec;118(3):428-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01074.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10594563 Free PMC article.
-
Aglepristone (RU534) administration to non-pregnant bitches in the mid-luteal phase induces early luteal regression.Theriogenology. 2010 Sep 1;74(4):672-81. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2010.03.021. Epub 2010 May 7. Theriogenology. 2010. PMID: 20452002 Clinical Trial.
-
[Interleukin-12 restores and promotes the T-cell immune function inhibited by 5-fluorouracil].Ai Zheng. 2007 Aug;26(8):801-8. Ai Zheng. 2007. PMID: 17697537 Chinese.
References
-
- Hoffmann B, Schuler G. Receptor blockers - general aspects with respect to their use in domestic animal reproduction. Anim Reprod Sci. 2000;60–61:295–312. - PubMed
-
- Rollón E, Millán Y, Martin De Las Mulas J. Effects of aglepristone, a progesterone receptor antagonist, in a dog with a vaginal fibroma. J Small Anim Pract. 2008;49:41–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

