A symbiotic relationship between epithelial and stromal stem cells
- PMID: 24284171
- PMCID: PMC3870754
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1320032110
A symbiotic relationship between epithelial and stromal stem cells
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
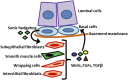
Comment on
-
Sonic hedgehog signals to multiple prostate stromal stem cells that replenish distinct stromal subtypes during regeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 17;110(51):20611-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315729110. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24218555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fuchs E, Tumbar T, Guasch G. Socializing with the neighbors: Stem cells and their niche. Cell. 2004;116(6):769–778. - PubMed
-
- Lu TL, et al. Conditionally ablated Pten in prostate basal cells promotes basal-to-luminal differentiation and causes invasive prostate cancer in mice. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(3):975–991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

