Inducing host protection in pneumococcal sepsis by preactivation of the Ashwell-Morell receptor
- PMID: 24284176
- PMCID: PMC3864324
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1313905110
Inducing host protection in pneumococcal sepsis by preactivation of the Ashwell-Morell receptor
Abstract
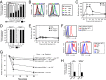
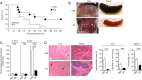
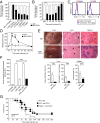
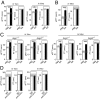
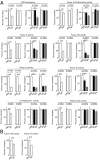
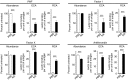
The endocytic Ashwell-Morell receptor (AMR) of hepatocytes detects pathogen remodeling of host glycoproteins by neuraminidase in the bloodstream and mitigates the lethal coagulopathy of sepsis. We have investigated the mechanism of host protection by the AMR during the onset of sepsis and in response to the desialylation of blood glycoproteins by the NanA neuraminidase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. We find that the AMR selects among potential glycoprotein ligands unmasked by microbial neuraminidase activity in pneumococcal sepsis to eliminate from blood circulation host factors that contribute to coagulation and thrombosis. This protection is attributable in large part to the rapid induction of a moderate thrombocytopenia by the AMR. We further show that neuraminidase activity in the blood can be manipulated to induce the clearance of AMR ligands including platelets, thereby preactivating a protective response in pneumococcal sepsis that moderates the severity of disseminated intravascular coagulation and enables host survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Levi M, Schultz M, van der Poll T. Sepsis and thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2010;36:367–377. - PubMed
-
- Marshall JC. Inflammation, coagulopathy, and the pathogenesis of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7) Suppl:S99–S106. - PubMed
-
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ. The failure of biologics in sepsis: Where do we stand? Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;42(Suppl):S45–S47. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC. The search for effective therapy for sepsis: Back to the drawing board? JAMA. 2011;306(23):2614–2615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

