Role of amino acid transporters in amino acid sensing
- PMID: 24284439
- PMCID: PMC3862456
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.113.070086
Role of amino acid transporters in amino acid sensing
Abstract
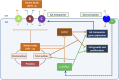
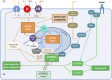
Amino acid (AA) transporters may act as sensors, as well as carriers, of tissue nutrient supplies. This review considers recent advances in our understanding of the AA-sensing functions of AA transporters in both epithelial and nonepithelial cells. These transporters mediate AA exchanges between extracellular and intracellular fluid compartments, delivering substrates to intracellular AA sensors. AA transporters on endosomal (eg, lysosomal) membranes may themselves function as intracellular AA sensors. AA transporters at the cell surface, particularly those for large neutral AAs such as leucine, interact functionally with intracellular nutrient-signaling pathways that regulate metabolism: for example, the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway, which promotes cell growth, and the general control non-derepressible (GCN) pathway, which is activated by AA starvation. Under some circumstances, upregulation of AA transporter expression [notably a leucine transporter, solute carrier 7A5 (SLC7A5)] is required to initiate AA-dependent activation of the mTORC1 pathway. Certain AA transporters may have dual receptor-transporter functions, operating as "transceptors" to sense extracellular (or intracellular) AA availability upstream of intracellular signaling pathways. New opportunities for nutritional therapy may include targeting of AA transporters (or mechanisms that upregulate their expression) to promote protein-anabolic signals for retention or recovery of lean tissue mass.
Figures

References
-
- Bröer S. Amino acid transport across mammalian intestinal and renal epithelia. Physiol Rev 2008;88:249–86. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs BC, Bode BP. Amino acid transporters ASCT2 and LAT1 in cancer: partners in crime? Semin Cancer Biol 2005;15:254–66. - PubMed
-
- Poncet N, Taylor PM. The role of amino acid transporters in nutrition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2013;16:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Verrey F, Closs EI, Wagner CA, Palacin M, Endou H, Kanai Y. CATs and HATs: the SLC7 family of amino acid transporters. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol 2004;447(5):532–42. - PubMed
-
- Jézégou A, Llinares E, Anne C. Kieffer-Jaquinod S, O'Regan S, Aupetit J, Chabli A, Sagné C, Debacker C, Chadefaux-Vekemans B, et al. Heptahelical protein PQLC2 is a lysosomal cationic amino acid exporter underlying the action of cysteamine in cystinosis therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012;109:E3434–43. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

