Maternal controlling feeding practices and girls' inhibitory control interact to predict changes in BMI and eating in the absence of hunger from 5 to 7 y
- PMID: 24284443
- PMCID: PMC3893722
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.113.063545
Maternal controlling feeding practices and girls' inhibitory control interact to predict changes in BMI and eating in the absence of hunger from 5 to 7 y
Abstract
Background: Mothers use a range of feeding practices to limit children's intake of palatable snacks (eg, keeping snacks out of reach, not bringing snacks into the home), but less is known about the effects of these practices on children's eating and weight outcomes.
Objective: The objective was to identify distinct feeding practice profiles and evaluate the interactive effects of these profiles and girls' temperament (inhibitory control and approach) on girls' eating behaviors and weight outcomes at 5 and 7 y.
Design: Participants included 180 mother-daughter dyads; measures were mothers' reports of controlling feeding practices and girls' height and weight, eating in the absence of hunger (EAH) at 5 y, and inhibitory control (a measure of behavioral inhibition) and approach (a measure of appetitive motivation) at 7 y.
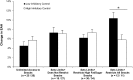
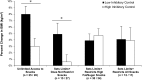
Results: Latent profile analysis of maternal feeding practices showed 4 feeding profiles based on maternal use of limit-setting practices and keeping snacks out of girls' physical reach, a restrictive practice: Unlimited Access to Snacks, Sets Limits+Does Not Restrict Snacks, Sets Limits+Restricts High Fat/Sugar Snacks, and Sets Limits+Restricts All Snacks. Girls whose mothers used Sets Limits+Restricts All Snacks had a higher approach and EAH at 5 y. Low inhibitory control girls whose mothers used Sets Limits+Restricts All Snacks or Unlimited Access to Snacks had greater increases in EAH and body mass index (BMI) from 5 to 7 y.
Conclusions: Effects of maternal control on girls' EAH and BMI may differ by the type of practice used (eg, limit-setting or restrictive practices). Girls with low inhibitory control were more susceptible to the negative effects of low and high control.
Figures
Comment in
-
Testing Satter's Division of Responsibility in Feeding in the context of restrictive snack-management practices.Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Sep;100(3):986-7. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.091512. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014. PMID: 25142891 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to EM Satter.Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Sep;100(3):987-8. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.092049. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014. PMID: 25142892 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fisher JO, Birch LL. Restricting access to foods and children's eating. Appetite 1999;32:405–19. - PubMed
-
- Fisher JO, Birch LL. Restricting access to palatable foods affects children's behavioral response, food selection, and intake. Am J Clin Nutr 1999;69:1264–72. - PubMed
-
- Houck GM. Maternal limit setting during toddlerhood, delay of gratification, and behavior problems at age five. Infant Ment Health J 2004;25:28–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

