Rate-limiting step analysis of the microbial desulfurization of dibenzothiophene in a model oil system
- PMID: 24284557
- PMCID: PMC3969791
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.25148
Rate-limiting step analysis of the microbial desulfurization of dibenzothiophene in a model oil system
Abstract
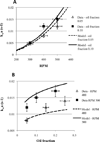
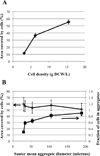
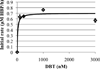
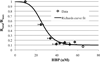
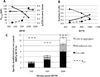
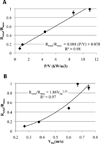
A mechanistic analysis of the various mass transport and kinetic steps in the microbial desulfurization of dibenzothiophene (DBT) by Rhodococcus erythropolis IGTS8 in a model biphasic (oil-water), small-scale system was performed. The biocatalyst was distributed into three populations, free cells in the aqueous phase, cell aggregates and oil-adhered cells, and the fraction of cells in each population was measured. The power input per volume (P/V) and the impeller tip speed (vtip ) were identified as key operating parameters in determining whether the system is mass transport controlled or kinetically controlled. Oil-water DBT mass transport was found to not be limiting under the conditions tested. Experimental results at both the 100 mL and 4 L (bioreactor) scales suggest that agitation leading to P/V greater than 10,000 W/ m(3) and/or vtip greater than 0.67 m/s is sufficient to overcome the major mass transport limitation in the system, which was the diffusion of DBT within the biocatalyst aggregates.
Keywords: Rhodococcus erythropolis IGTS8; aggregation; biodesulfurization; dibenzothiophene; power input per volume; rate-limiting step.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic engineering of hydrophobic Rhodococcus opacus for biodesulfurization in oil-water biphasic reaction mixtures.J Biosci Bioeng. 2012 Mar;113(3):360-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.10.017. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012. PMID: 22099375
-
Biodesulfurization of a system containing synthetic fuel using Rhodococcus erythropolis ATCC 4277.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Nov;174(6):2079-85. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-1189-3. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25163887
-
An Evaluation of Kinetic Models in the Biodesulfurization of Synthetic Oil by Rhodococcus erythropolis ATCC 4277.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015 Oct;177(3):759-70. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1764-2. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26201481
-
Desulphurisation of benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene by actinomycete organisms belonging to the genus Rhodococcus, and related taxa.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1998 Jul-Oct;74(1-3):119-32. doi: 10.1023/a:1001724516342. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1998. PMID: 10068795 Review.
-
Desulfurization and desulfonation: applications of sulfur-controlled gene expression in bacteria.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Nov;57(4):460-6. doi: 10.1007/s002530100800. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11762590 Review.
Cited by
-
Biocatalytic desulfurization of thiophenic compounds and crude oil by newly isolated bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2015 Feb 13;6:112. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00112. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25762990 Free PMC article.
-
Biodesulfurization of Fossil Fuels: Analysis and Prospective.F1000Res. 2023 Sep 8;12:1116. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.133427.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 38533421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics and Metabolomics Analyses to Elucidate the Desulfurization Pathway of Chelatococcus sp.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0153547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153547. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100386 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Biochemical Characterization of BdsA from Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B, a Key Enzyme in the "4S" Desulfurization Pathway.Front Microbiol. 2018 Feb 15;9:231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00231. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29497411 Free PMC article.
-
Differential desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by newly identified MTCC strains: Influence of Operon Array.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 8;13(3):e0192536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192536. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29518089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boltes K, del Aguila RA, Garcia-Calvo E. Effect of mass transfer on biodesulfurization kinetics of alkyalted forms of dibenzothiophene by Pseudomonas putida CECT5279. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2012;88:422–431.
-
- Caro A, Boltes K, Leton P, Garcia-Calvo E. Description of by-product inhibition effects on biodesulfuriation of dibenzothiophene in biphasic media. Biodegradation. 2008;19:599–611. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Zhang WJ, Cai YB, Zhang Y, Li W. Elucidation of 2-hydroxybiphenyl effect on dibenzothiophene desulfurization by Microbacterium sp. strain ZD-M2. Biores Tech. 2008;99:6928–6933. - PubMed
-
- Coulaloglou CA, Tavlarides LL. Drop Size Distributions and Coalescence Frequencies of Liquid-Liquid Dispersions in Flow Vessels. AICHe Journal. 1976;22(2):289–297.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

