Purinergic 2X receptors play a role in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in rats with peripheral artery insufficiency
- PMID: 24285113
- PMCID: PMC3920134
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00762.2013
Purinergic 2X receptors play a role in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in rats with peripheral artery insufficiency
Abstract
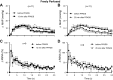
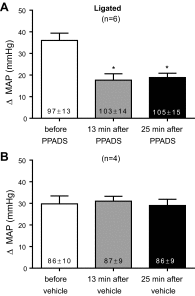
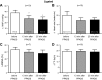
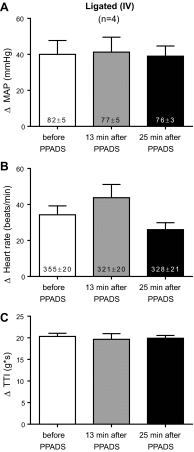
Purinergic 2X (P2X) receptors on the endings of thin fiber afferents have been shown to play a role in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in cats. In this study, we attempted to extend this finding to decerebrated, unanesthetized rats whose femoral arteries were either freely perfused or were ligated 72 h before the start of the experiment. We first established that our dose of pyridoxal phosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid (PPADS; 10 mg/kg), a P2X receptor antagonist, attenuated the pressor response to α,β-methylene ATP (10 μg/kg), a P2X receptor agonist. We then compared the exercise pressor reflex before and after infusing PPADS into the arterial supply of the hindlimb muscles that were statically contracted. In rats with freely perfused femoral arteries, the peak pressor responses to contraction were not significantly attenuated by PPADS (before PPADS: 19 ± 2 mmHg, 13 min after PPADS: 17 ± 2 mmHg, and 25 min after PPADS: 17 ± 3 mmHg). Likewise, the cardioaccelerator and renal sympathetic nerve responses were not significantly attenuated. In contrast, we found that in rats whose femoral arteries were ligated PPADS significantly attenuated the peak pressor responses to contraction (before PPADS: 37 ± 5 mmHg, 13 min after PPADS: 27 ± 6 mmHg, and 25 min after PPADS: 25 ± 5 mmHg; P < 0.05). Heart rate was not significantly attenuated, but renal SNA was at certain time points over the 30-s contraction period. We conclude that P2X receptors play a substantial role in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in rats whose femoral arteries were ligated but play only a minimal role in evoking the reflex in rats whose femoral arteries were freely perfused.
Keywords: PPADS; autonomic nervous system; renal sympathetic activity; thin fiber muscle afferents; α,β-methylene ATP.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Combined, but not individual, blockade of ASIC3, P2X, and EP4 receptors attenuates the exercise pressor reflex in rats with freely perfused hindlimb muscles.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Dec 1;119(11):1330-6. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00630.2015. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 26472871 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal P2X receptor modulates reflex pressor response to activation of muscle afferents.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 May;288(5):H2238-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01095.2004. Epub 2004 Dec 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15615840
-
Role played by interleukin-6 in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in decerebrate rats: effect of femoral artery ligation.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;309(1):H166-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00195.2015. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25910806 Free PMC article.
-
Design and pharmacology of selective P2-purinoceptor antagonists.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):341-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00049.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131412 Review.
-
Mechanosensitive channels in the mechanical component of the exercise pressor reflex.Auton Neurosci. 2023 Dec;250:103128. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2023.103128. Epub 2023 Oct 29. Auton Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37925831 Review.
Cited by
-
Exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in type 2 diabetes: Potential role of oxidative stress.Auton Neurosci. 2019 Dec;222:102591. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2019.102591. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Auton Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31669797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The exercise pressor reflex: An update.Clin Auton Res. 2022 Aug;32(4):271-290. doi: 10.1007/s10286-022-00872-3. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Clin Auton Res. 2022. PMID: 35727398 Review.
-
ASIC1a does not play a role in evoking the metabolic component of the exercise pressor reflex in a rat model of peripheral artery disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Jul 1;319(1):H171-H182. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00257.2020. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32502377 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal neurocirculatory control during exercise in humans with chronic renal failure.Auton Neurosci. 2015 Mar;188:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2014.10.013. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Auton Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25458430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrathecal injection of brilliant blue G, a P2X7 antagonist, attenuates the exercise pressor reflex in rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):R223-R232. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00093.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32609538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baccelli G, Reggiani P, Mattioli A, Corbellini E, Garducci S, Catalano M. The exercise pressor reflex and changes in radial arterial pressure and heart rate during walking in patients with arteriosclerosis obliterans. Angiology 50: 361–374, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Bradbury EJ, Burnstock G, McMahon SB. The expression of P2X3 purinoreceptors in sensory neurons: effects of axotomy and glial-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Cell Neurosci 12: 256–268, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G, Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoreceptor? Gen Pharmacol 16: 433–440, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Cook SP, Vulchanova L, Hargreaves KM, Elde R, McCleskey EW. Distinct ATP receptors on pain-sensing and stretch-sensing neurons. Nature 387: 505–508, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

