Cardiovascular effect of angiotensin-(1-12) in the caudal ventrolateral medullary depressor area of the rat
- PMID: 24285114
- PMCID: PMC3920147
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00628.2013
Cardiovascular effect of angiotensin-(1-12) in the caudal ventrolateral medullary depressor area of the rat
Abstract
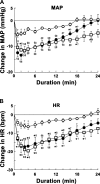
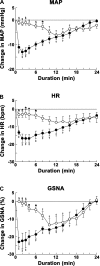
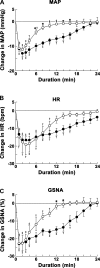
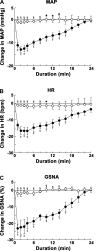
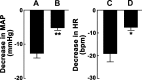
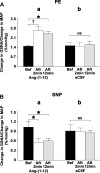
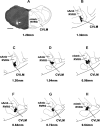
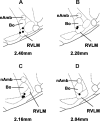
Angiotensin (ANG)-(1-12) excites neurons via ANG II type 1 receptors (AT1Rs), which are present in the caudal ventrolateral medullary depressor area (CVLM). We hypothesized that microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the CVLM may elicit decreases in mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), and sympathetic nerve activity. This hypothesis was tested in urethane-anesthetized adult male Wistar rats. Microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the CVLM elicited decreases in MAP, HR, and greater splanchnic nerve activity (GSNA). ANG-(1-12)-induced responses consisted of initial (first 1-8 min) and delayed (8-24 min) phases. Prior microinjections of losartan, A-779, and captopril into the CVLM blocked initial, delayed, and both phases of ANG-(1-12) responses, respectively. Blockade of GABA receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medullary pressor area (RVLM) attenuated cardiovascular responses elicited by microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the ipsilateral CVLM. Microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the CVLM potentiated the reflex decreases and attenuated the reflex increases in GSNA elicited by intravenous injections of phenylephrine and sodium nitroprusside, respectively. These results indicate that microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the CVLM elicit decreases in MAP, HR, and GSNA. Initial and delayed phases of these responses are mediated via ANG II and ANG-(1-7), respectively; the effects of ANG II and ANG-(1-7) are mediated via AT1Rs and Mas receptors, respectively. Captopril blocked both phases of ANG-(1-12) responses, indicating that angiotensin-converting enzyme is important in mediating these responses. GABA receptors in the RVLM partly mediate the cardiovascular responses to microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the CVLM. Microinjections of ANG-(1-12) into the CVLM modulate baroreflex responses.
Keywords: GABAergic neurons; Mas receptors; angiotensin II receptors; baroreflex; sympathetic nerve activity.
Figures
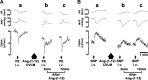
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-(1-12) in the rostral ventrolateral medullary pressor area of the rat elicits sympathoexcitatory responses.Exp Physiol. 2013 Jan;98(1):94-108. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.067116. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Exp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22707504 Free PMC article.
-
Baroreflex modulation by angiotensins at the rat rostral and caudal ventrolateral medulla.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006 Apr;290(4):R1027-34. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00852.2004. Epub 2005 Nov 23. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16306161
-
Angiotensin-(1-7) antagonist, A-779, microinjection into the caudal ventrolateral medulla of renovascular hypertensive rats restores baroreflex bradycardia.Peptides. 2009 Oct;30(10):1921-7. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.06.028. Epub 2009 Jul 3. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19577603
-
Role of the caudal pressor area in the regulation of sympathetic vasomotor tone.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2008 Jul;41(7):557-62. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2008000700002. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2008. PMID: 18719736 Review.
-
The baroreflex and beyond: control of sympathetic vasomotor tone by GABAergic neurons in the ventrolateral medulla.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002 May-Jun;29(5-6):514-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2002.03665.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12010201 Review.
Cited by
-
Attenuation of angiotensin type 2 receptor function in the rostral ventrolateral medullary pressor area of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016;38(2):209-17. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2015.1081229. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26818039 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin (1-12) in Humans With Normal Blood Pressure and Primary Hypertension.Hypertension. 2021 Mar 3;77(3):882-890. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16514. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Hypertension. 2021. PMID: 33461312 Free PMC article.
-
Intracrine angiotensin II functions originate from noncanonical pathways in the human heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):H404-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00219.2016. Epub 2016 May 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27233763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoneutralization of human angiotensin-(1-12) with a monoclonal antibody in a humanized model of hypertension.Peptides. 2022 Mar;149:170714. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170714. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Peptides. 2022. PMID: 34933010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen AM, Mendelsohn FAO, Gieroba ZJ, Blessing WW. Vasopressin release following microinjection of angiotensin II into the caudal ventrolateral medulla oblongata in the anaesthetized rabbit. J Neuroendocrinol 2: 867–873, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Alzamora AC, Santos RA, Campagnole-Santos MJ. Hypotensive effect of ANG II and ANG-(1–7) at the caudal ventrolateral medulla involves different mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283: R1187–R1195, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Alzamora AC, Santos RA, Campagnole-Santos MJ. Baroreflex modulation by angiotensins at the rat rostral and caudal ventrolateral medulla. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290: R1027–R1034, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

