Phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain has minimal effect on kinetics and distribution of orientations of cross bridges of rabbit skeletal muscle
- PMID: 24285364
- PMCID: PMC3921311
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00382.2013
Phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain has minimal effect on kinetics and distribution of orientations of cross bridges of rabbit skeletal muscle
Abstract
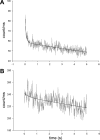
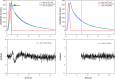
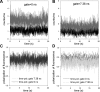
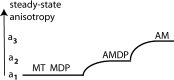
Force production in muscle results from ATP-driven cyclic interactions of myosin with actin. A myosin cross bridge consists of a globular head domain, containing actin and ATP-binding sites, and a neck domain with the associated light chain 1 (LC1) and the regulatory light chain (RLC). The actin polymer serves as a "rail" over which myosin translates. Phosphorylation of the RLC is thought to play a significant role in the regulation of muscle relaxation by increasing the degree of skeletal cross-bridge disorder and increasing muscle ATPase activity. The effect of phosphorylation on skeletal cross-bridge kinetics and the distribution of orientations during steady-state contraction of rabbit muscle is investigated here. Because the kinetics and orientation of an assembly of cross bridges (XBs) can only be studied when an individual XB makes a significant contribution to the overall signal, the number of observed XBs was minimized to ∼20 by limiting the detection volume and concentration of fluorescent XBs. The autofluorescence and photobleaching from an ex vivo sample was reduced by choosing a dye that was excited in the red and observed in the far red. The interference from scattering was eliminated by gating the signal. These techniques decrease large uncertainties associated with determination of the effect of phosphorylation on a few molecules ex vivo with millisecond time resolution. In spite of the remaining uncertainties, we conclude that the state of phosphorylation of RLC had no effect on the rate of dissociation of cross bridges from thin filaments, on the rate of myosin head binding to thin filaments, and on the rate of power stroke. On the other hand, phosphorylation slightly increased the degree of disorder of active cross bridges.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of a myosin regulatory light chain mutation K104E on actin-myosin interactions.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):H1248-57. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00834.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25770245 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the regulatory light chains of myosin affects Ca2+ sensitivity of skeletal muscle contraction.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002 Apr;92(4):1661-70. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00858.2001. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002. PMID: 11896035
-
Altered kinetics of contraction in skeletal muscle fibers containing a mutant myosin regulatory light chain with reduced divalent cation binding.Biophys J. 1996 Jul;71(1):341-50. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79231-7. Biophys J. 1996. PMID: 8804617 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of contraction in striated muscle.Physiol Rev. 2000 Apr;80(2):853-924. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2000.80.2.853. Physiol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10747208 Review.
-
Modulation of Skeletal Muscle Contraction by Myosin Phosphorylation.Compr Physiol. 2016 Dec 6;7(1):171-212. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150044. Compr Physiol. 2016. PMID: 28135003 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluorescent Self-Threaded Peptide Probes for Biological Imaging.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Dec 21;59(52):23740-23747. doi: 10.1002/anie.202009599. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32930474 Free PMC article.
-
The spatial distribution of actin and mechanical cycle of myosin are different in right and left ventricles of healthy mouse hearts.Biochemistry. 2014 Dec 9;53(48):7641-9. doi: 10.1021/bi501175s. Epub 2014 Nov 30. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25488019 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain of myosin in striated muscle: methodological perspectives.Eur Biophys J. 2016 Dec;45(8):779-805. doi: 10.1007/s00249-016-1128-z. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Eur Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27084718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-molecule characterization of a bright and photostable deep-red fluorescent squaraine-figure-eight (SF8) dye.Dyes Pigm. 2023 Feb;210:111031. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.111031. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Dyes Pigm. 2023. PMID: 36643871 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of skeletal muscle myosin metabolic states in hibernating mammals.Elife. 2024 May 16;13:RP94616. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94616. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38752835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagshaw CR. Muscle Contraction. London: Chapman & Hall, 1982
-
- Bershitsky SY, Tsaturyan AK, Bershitskaya ON, Mashanov GI, Brown P, Burns R, Ferenczi MA. Muscle force is generated by myosin heads stereospecifically attached to actin. Nature 388: 186–190, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Borejdo J, Midde K. Rapid measurements of orientation and rotation of a small number of cross-bridges in ex vivo muscle. In: Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy Techniques, edited by Conn M, New York: Elesevier, In press
-
- Bracewell R. The Fourier Transform and Its Applications. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1965
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

