Transepithelial transport of Fc-targeted nanoparticles by the neonatal fc receptor for oral delivery
- PMID: 24285486
- PMCID: PMC4023672
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007049
Transepithelial transport of Fc-targeted nanoparticles by the neonatal fc receptor for oral delivery
Abstract
Nanoparticles are poised to have a tremendous impact on the treatment of many diseases, but their broad application is limited because currently they can only be administered by parenteral methods. Oral administration of nanoparticles is preferred but remains a challenge because transport across the intestinal epithelium is limited. We show that nanoparticles targeted to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), which mediates the transport of immunoglobulin G antibodies across epithelial barriers, are efficiently transported across the intestinal epithelium using both in vitro and in vivo models. In mice, orally administered FcRn-targeted nanoparticles crossed the intestinal epithelium and reached systemic circulation with a mean absorption efficiency of 13.7%*hour compared with only 1.2%*hour for nontargeted nanoparticles. In addition, targeted nanoparticles containing insulin as a model nanoparticle-based therapy for diabetes were orally administered at a clinically relevant insulin dose of 1.1 U/kg and elicited a prolonged hypoglycemic response in wild-type mice. This effect was abolished in FcRn knockout mice, indicating that the enhanced nanoparticle transport was specifically due to FcRn. FcRn-targeted nanoparticles may have a major impact on the treatment of many diseases by enabling drugs currently limited by low bioavailability to be efficiently delivered though oral administration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
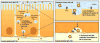
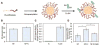
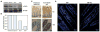
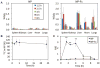

References
-
- Wang AZ, Langer R, Farokhzad OC. Nanoparticle Delivery of Cancer Drugs. Annu Rev Med. 2012;63:185–198. - PubMed
-
- Hrkach J, Von Hoff D, Ali MM, Andrianova E, Auer J, Campbell T, De Witt D, Figa M, Figueiredo M, Horhota A, Low S, McDonnell K, Peeke E, Retnarajan B, Sabnis A, Schnipper E, Song JJ, Song YH, Summa J, Tompsett D, Troiano G, Van Geen Hoven T, Wright J, LoRusso P, Kantoff PW, Bander NH, Sweeney C, Farokhzad OC, Langer R, Zale S. Preclinical Development and Clinical Translation of a PSMA-Targeted Docetaxel Nanoparticle with a Differentiated Pharmacological Profile. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:128ra39–128ra39. - PubMed
-
- Borner MM, Schoffski P, de Wit R, Caponigro F, Comella G, Sulkes A, Greim G, Peters GJ, van der Born K, Wanders J, de Boer RF, Martin C, Fumoleau P. Patient preference and pharmacokinetics of oral modulated UFT versus intravenous fluorouracil and leucovorin: a randomised crossover trial in advanced colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:349–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201000045C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK0034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB015419/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U54 CA151884-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EB000244/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB000244/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB015419-01/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000244/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151884/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54-CA151884/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK53056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK053056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

