Correlate of immune protection against HSV-1 genital disease in vaccinated women
- PMID: 24285844
- PMCID: PMC3935479
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jit651
Correlate of immune protection against HSV-1 genital disease in vaccinated women
Abstract
Background: Previously we conducted a double-blind controlled, randomized efficacy field trial of gD-2 HSV vaccine adjuvanted with ASO4 in 8323 women. Subjects had been previously selected to be seronegative for HSV-1 and HSV-2. We found that vaccine was 82% protective against HSV-1 genital disease, but offered no significant protection against HSV-2 genital disease.
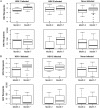
Methods: To better understand the results of the efficacy study, post-vaccination anti-gD-2 antibody concentrations from all HSV infected subjects and matched uninfected controls were measured. Three models were used to determine whether thes responses correlated with protection against HSV infection or disease. Similarly, cellular immune responses from a subset of subjects and matched controls were evaluated for a correlation with HSV protection.
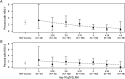
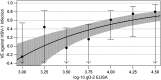
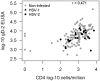
Results: Antibodies to gD-2 correlated with protection against HSV-1 infection with higher antibody concentration associated with higher efficacy. Cellular immune responses to gD-2 did not correlate with protection.
Conclusions: The protection against HSV-1 infection observed in the Herpevac Trial for Women was associated with antibodies directed against the vaccine. Clinical Trials Registration NCT00057330.
Keywords: HSV vaccine; protective antibodies; vaccine efficacy.
Figures

Comment in
-
A paradigm shift: vaccine-induced antibodies as an immune correlate of protection against herpes simplex virus type 1 genital herpes.J Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;209(6):813-5. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit658. Epub 2013 Nov 27. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24285847 No abstract available.
References
-
- Parsons LS. Performing a 1:N Case Control Match on Propensity Score. Proceedings of the Twenty Ninth Annual SAS Users Group International Conference; Cary, NC. SAS Institute Inc.; 2004.
-
- Ashley R, Cent A, Maggs V, Nahmias A, Corey L. Inability of enzyme immunoassays to discriminate between infections with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:520–6. - PubMed
-
- Maecker HT, Maino VC, Picker LJ. Immunofluorescence analysis of T-cell responses in health and disease. J Clin Immunol. 2000;20:391–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

