Propagating neocortical gamma bursts are coordinated by traveling alpha waves
- PMID: 24285891
- PMCID: PMC4262700
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2455-13.2013
Propagating neocortical gamma bursts are coordinated by traveling alpha waves
Abstract
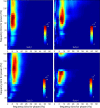
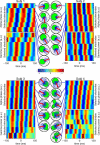
Neocortical neuronal activity is characterized by complex spatiotemporal dynamics. Although slow oscillations have been shown to travel over space in terms of consistent phase advances, it is unknown how this phenomenon relates to neuronal activity in other frequency bands. We here present electrocorticographic data from three male and one female human subject and demonstrate that gamma power is phase locked to traveling alpha waves. Given that alpha activity has been proposed to coordinate neuronal processing reflected in the gamma band, we suggest that alpha waves are involved in coordinating neuronal processing in both space and time.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander DM, Jurica P, Trengove C, Nikolaev AR, Gepshtein S, Zvyagintsev M, Mathiak K, Schulze-Bonhage A, Ruescher J, Ball T, van Leeuwen C. Traveling waves and trial averaging: the nature of single-trial and averaged brain responses in large-scale cortical signals. Neuroimage. 2013;73:95–112. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartlett MS. Smoothing periodograms from time-series with continuous spectra. Nature. 1948;161:686–687. doi: 10.1038/161686a0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
