Alleviating memory impairment through distraction
- PMID: 24285905
- PMCID: PMC6618708
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1797-13.2013
Alleviating memory impairment through distraction
Abstract
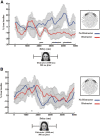
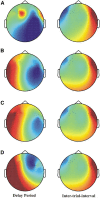
Distraction typically has a negative impact on memory for recent events and patients with existing memory impairment are particularly vulnerable to distractor interference. In contrast, here we establish a beneficial effect for distractor presentation in humans for both patients with memory impairment due to bilateral hippocampal lesions and healthy adults with low memory performance. Recognition memory for images of place scenes, which had to be memorized for short delay periods was significantly improved with the presentation of a distractor face during the delay. Magnetoencephalography recordings of neural oscillations in the theta frequency range obtained in healthy adults suggest that this memory improvement results from the interruption of rehearsal by the distractor. Our results highlight circumstances where active memory rehearsal may paradoxically increase memory impairments and distraction alleviates these memory deficits in patients with hippocampal injury and healthy adults.
Figures
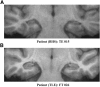

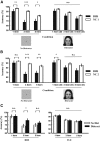
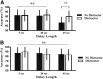
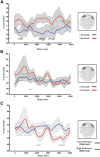
Similar articles
-
Functional substrate for memory function differences between patients with left and right mesial temporal lobe epilepsy associated with hippocampal sclerosis.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 Oct;51:251-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.07.032. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 26300534
-
Medial temporal theta/alpha power enhancement precedes successful memory encoding: evidence based on intracranial EEG.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 6;31(14):5392-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3668-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21471374 Free PMC article.
-
Extent of Single-Neuron Activity Modulation by Hippocampal Interictal Discharges Predicts Declarative Memory Disruption in Humans.J Neurosci. 2020 Jan 15;40(3):682-693. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1380-19.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31754015 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbances of septohippocampal theta oscillations in the epileptic brain: reasons and consequences.Exp Neurol. 2013 Sep;247:314-27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.01.029. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23384663 Review.
-
Behavioral significance of hippocampal θ oscillations: looking elsewhere to find the right answers.J Neurophysiol. 2011 Aug;106(2):497-9. doi: 10.1152/jn.00358.2011. Epub 2011 May 11. J Neurophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21562189 Review.
Cited by
-
Do cognitive load and ADHD traits affect the tendency to prioritise social information in scenes?Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2022 Oct;75(10):1904-1918. doi: 10.1177/17470218211066475. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2022. PMID: 34844477 Free PMC article.
-
A Cognitive Paradigm to Investigate Interference in Working Memory by Distractions and Interruptions.J Vis Exp. 2015 Jul 16;(101):e52226. doi: 10.3791/52226. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26273742 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
