Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in the airway: role in airway disease
- PMID: 24286227
- PMCID: PMC4009002
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12538
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in the airway: role in airway disease
Abstract
Over the last few decades, there has been an explosion of scientific publications reporting the many and varied roles of transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels in physiological and pathological systems throughout the body. The aim of this review is to summarize the existing literature on the role of TRP channels in the lungs and discuss what is known about their function under normal and diseased conditions. The review will focus mainly on the pathogenesis and symptoms of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the role of four members of the TRP family: TRPA1, TRPV1, TRPV4 and TRPM8. We hope that the article will help the reader understand the role of TRP channels in the normal airway and how their function may be changed in the context of respiratory disease.
Keywords: COPD; TRP channels; airway; asthma.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
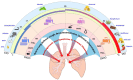
 = Osmolar.
= Osmolar. = Acid.
= Acid.References
-
- Abbott-Banner K, Poll C, Verkuyl JM. Targeting TRP channels in airway disorders. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13:310–321. - PubMed
-
- Agopyan N, Head J, Yu S, Simon SA. TRPV1 receptors mediate particulate matter-induced apoptosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Ahluwalia J, Urban L, Capogna M, Bevan S, Nagy I. Cannabinoid 1 receptors are expressed in nociceptive primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience. 2000;100:685–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

