Lifetime prevalence, associated factors, and circumstances of non-volitional sex in women and men in Britain: findings from the third National Survey of Sexual Attitudes and Lifestyles (Natsal-3)
- PMID: 24286789
- PMCID: PMC3898964
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62300-4
Lifetime prevalence, associated factors, and circumstances of non-volitional sex in women and men in Britain: findings from the third National Survey of Sexual Attitudes and Lifestyles (Natsal-3)
Abstract
Background: Sexual violence is increasingly recognised as a public health issue. Information about prevalence, associated factors, and consequences for health in the population of Britain (England, Scotland, and Wales) is scarce. The third National Survey of Sexual Health Attitudes and Lifestyles (Natsal-3) is the first of the Natsal surveys to include questions about sexual violence and the first population-based survey in Britain to explore the issue outside the context of crime.
Methods: Between Sept 6, 2010, and Aug 31, 2012, we did a probability sample survey of women and men aged 16-74 years living in Britain. We asked participants about their experience of sex against their will since age 13 years and the circumstances surrounding the most recent occurrence. We explored associations between ever experiencing non-volitional sex and a range of sociodemographic, health, and behavioural factors. We used logistic regression to estimate age-adjusted odds ratios to analyse factors associated with the occurrence of completed non-volitional sex in women and men.
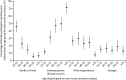
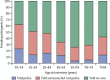
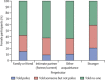
Findings: We interviewed 15,162 people. Completed non-volitional sex was reported by 9·8% (95% CI 9·0-10·5) of women and 1·4% (1·1-1·7) of men. Median age (interdecile range) at most recent occurrence was 18 years (14-32) for women and 16 years (13-30) for men. Completed non-volitional sex varied by family structure and, in women, by age, education, and area-level deprivation. It was associated with poor health, longstanding illness or disability, and treatment for mental health conditions, smoking, and use of non-prescription drugs in the past year in both sexes, and with binge drinking in women. Completed non-volitional sex was also associated with reporting of first heterosexual intercourse before 16 years of age, same-sex experience, more lifetime sexual partners, ever being diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, and low sexual function in both sexes, and, in women, with abortion and pregnancy outcome before 18 years of age. In most cases, the person responsible was known to the individual, although the nature of the relationship differed by age at most recent occurrence. Participants who were younger at interview were more likely to have told someone about the event and to have reported it to the police than were older participants.
Interpretation: These data provide the first population prevalence estimates of non-volitional sex in Britain. We showed it to be mainly an experience of young age and strongly associated with a range of adverse health outcomes in both women and men.
Funding: Grants from the UK Medical Research Council and the Wellcome Trust, with support from the Economic and Social Research Council and the Department of Health.
Copyright © 2013 Macdowall et al. Open Access article distributed under the terms of CC BY. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Natsal and sexual violence in Britain.Lancet. 2014 Mar 8;383(9920):866-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60438-4. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24607094 No abstract available.
-
Natsal and sexual violence in Britain--authors' reply.Lancet. 2014 Mar 8;383(9920):867. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60439-6. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24607096 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . Global and regional estimates of violence against women: prevalence and health effects of intimate partner violence and non-partner sexual violence. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2013.
-
- Krug E, Dahlberg L, Mercy J, Zwi A, Lozano R. World report on violence and health. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2002.
-
- Garcia-Moreno C, Jansen H, Ellsberg M, Heise L, Watts C, for the WHO Multi-country Study on Women's Health and Domestic Violence against Women Study Team Prevalence of intimate partner violence: findings from the WHO multi-country study on women's health and domestic violence. Lancet. 2006;368:1260–1269. - PubMed
-
- Jina R, Thomas L. Health consequences of sexual violence against women. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2013;27:15–26. - PubMed
-
- Ellsberg M, Jansen H, Heise L, Watts C, Garcia-Moreno C, for the WHO Multi-country Study on Women's Health and Domestic Violence against Women Study Team Intimate partner violence and women's physical and mental health in the WHO multi-country study on women's health and domestic violence: an observational study. Lancet. 2008;371:1165–1172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

