Loss of dE2F compromises mitochondrial function
- PMID: 24286825
- PMCID: PMC3866969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.10.002
Loss of dE2F compromises mitochondrial function
Abstract
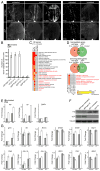
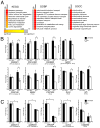
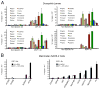
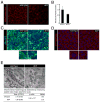
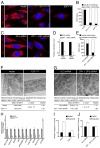
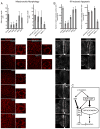
E2F/DP transcription factors regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Here, we investigated the mechanism of the resistance of Drosophila dDP mutants to irradiation-induced apoptosis. Contrary to the prevailing view, this is not due to an inability to induce the apoptotic transcriptional program, because we show that this program is induced; rather, this is due to a mitochondrial dysfunction of dDP mutants. We attribute this defect to E2F/DP-dependent control of expression of mitochondria-associated genes. Genetic attenuation of several of these E2F/DP targets mimics the dDP mutant mitochondrial phenotype and protects against irradiation-induced apoptosis. Significantly, the role of E2F/DP in the regulation of mitochondrial function is conserved between flies and humans. Thus, our results uncover a role of E2F/DP in the regulation of mitochondrial function and demonstrate that this aspect of E2F regulation is critical for the normal induction of apoptosis in response to irradiation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cell death: E2Ffects on mitochondria.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;15(1):6. doi: 10.1038/nrm3726. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24355987 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abdelwahid E, Yokokura T, Krieser RJ, Balasundaram S, Fowle WH, White K. Mitochondrial disruption in Drosophila apoptosis. Dev Cell. 2007;12:793–806. - PubMed
-
- Asano M, Nevins JR, Wharton RP. Ectopic E2F expression induces S phase and apoptosis in Drosophila imaginal discs. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1422–1432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

