Unmet health care needs of older people: prevalence and predictors in a French cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 24287029
- PMCID: PMC4168041
- DOI: 10.1093/eurpub/ckt179
Unmet health care needs of older people: prevalence and predictors in a French cross-sectional survey
Abstract
Background: Unmet health care needs are associated with negative health outcomes, yet there is a paucity of data on this problem among older people.
Objective: To identify unmet health care needs and associated factors among older people in France.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional population study of people aged 70 years or older in which 2350 respondents were interviewed in 2008-10. During a standardized interview, a nurse examined health problems, functional abilities and use of health care resources. Unmet health care needs were defined as situations in which a participant needed health care and did not receive it.
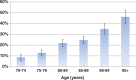
Results: The mean age was 83.2 ± 7.4 years. Almost all participants reporting a chronic disease (98.6%) had consulted a physician in the previous 6 months. Unmet health care needs were found in 23.0% of the sample and mainly consisted of lack of dental care (prevalence of 17.7%), followed by lack of management of visual or hearing impairments (prevalence of 4.4% and 3.1%, respectively). Age was the main factor associated with unmet health care needs [compared with people aged 70-79: odds ratio80-89 years = 2.26 (1.70-3.03), odds ratio90 years and over = 3.85 (2.71-5.45)]. Other associated factors were regular smoking, homebound status, poor socioeconomic conditions, depression, limitations in instrumental activities of daily living and low medical density.
Conclusion: Unmet health care needs affect almost one-quarter of older people in France. Efforts should be made to improve oral health and develop home care, especially for the oldest-olds.
© The Author 2013. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Public Health Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unmet health care needs and mortality among Spanish elderly.Am J Public Health. 1997 Mar;87(3):365-70. doi: 10.2105/ajph.87.3.365. Am J Public Health. 1997. PMID: 9096535 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of access, utilization and need for oral health care by the non-institutionalized and institutionalized elderly on the dental delivery system.J Dent Educ. 1993 Dec;57(12):876-87. J Dent Educ. 1993. PMID: 8263235 Review.
-
Significant unmet oral health needs of homebound elderly adults.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Jan;63(1):151-7. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13181. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015. PMID: 25537919 Free PMC article.
-
Unmet needs for home and community-based services among persons with disabilities in Massachusetts.Disabil Health J. 2011 Oct;4(4):219-28. doi: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2011.08.003. Disabil Health J. 2011. PMID: 22014669
-
[Micro data on the demand for care of dependent older people in Italy: A review of available sources].Epidemiol Prev. 2024 Jul-Oct;48(4-5):347-355. doi: 10.19191/EP24.4-5.A719.098. Epidemiol Prev. 2024. PMID: 39434643 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Morbidities, health problems, health care seeking and utilization behaviour among elderly residing on urban areas of eastern Nepal: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 7;17(9):e0273101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273101. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36070314 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective cross-sectional study examining the association between loneliness and unmet healthcare needs among middle-aged and older adults using the Canadian Longitudinal Study of Aging (CLSA).BMJ Open. 2023 Mar 14;13(3):e068769. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068769. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 36918248 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Health and Unmet Dental Care Needs on the Health-Related Quality of Life in Korea Older Adults: A Nationwide Study.Iran J Public Health. 2024 Jun;53(6):1304-1312. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39430148 Free PMC article.
-
What are the factors affecting older adults' experience of unmet healthcare needs amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea?BMC Geriatr. 2023 Aug 25;23(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04208-2. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37626287 Free PMC article.
-
Universal health coverage in the context of population ageing: catastrophic health expenditure and unmet need for healthcare.Health Econ Rev. 2024 Jan 30;14(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13561-023-00475-2. Health Econ Rev. 2024. PMID: 38289516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Institut canadien d’information sur la santé (ICIS). Les soins de santé au Canada 2001. Ottawa, Institut canadien d’information sur la santé 2001 (cited 2012). Available at: https://secure.cihi.ca/estore/productFamily.htm?locale=fr&pf=PFC105&lang....
-
- Chevreul K, Durand-Zaleski I, Bahrami S, et al. France: health system review. Health Syst Trans. 2010;12:1–291. - PubMed
-
- Sirven N, Or Z. The Individual and the Welfare State: Life Histories in Europe. Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Disparities in Regular Health Care Utilisation in Europe. pp. 241–54.
-
- Comptes nationaux de la santé 2010 (cited 2012). Available at: http://www.drees.sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/comptes_nationaux_sante_2010.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources