A label-free microfluidic biosensor for activity detection of single microalgae cells based on chlorophyll fluorescence
- PMID: 24287532
- PMCID: PMC3892884
- DOI: 10.3390/s131216075
A label-free microfluidic biosensor for activity detection of single microalgae cells based on chlorophyll fluorescence
Abstract
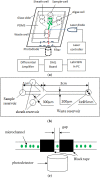
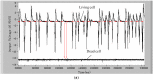
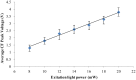
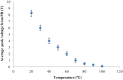
Detection of living microalgae cells is very important for ballast water treatment and analysis. Chlorophyll fluorescence is an indicator of photosynthetic activity and hence the living status of plant cells. In this paper, we developed a novel microfluidic biosensor system that can quickly and accurately detect the viability of single microalgae cells based on chlorophyll fluorescence. The system is composed of a laser diode as an excitation light source, a photodiode detector, a signal analysis circuit, and a microfluidic chip as a microalgae cell transportation platform. To demonstrate the utility of this system, six different living and dead algae samples (Karenia mikimotoi Hansen, Chlorella vulgaris, Nitzschia closterium, Platymonas subcordiformis, Pyramidomonas delicatula and Dunaliella salina) were tested. The developed biosensor can distinguish clearly between the living microalgae cells and the dead microalgae cells. The smallest microalgae cells that can be detected by using this biosensor are 3 μm ones. Even smaller microalgae cells could be detected by increasing the excitation light power. The developed microfluidic biosensor has great potential for in situ ballast water analysis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel Electrokinetic Microfluidic Detector for Evaluating Effectiveness of Microalgae Disinfection in Ship Ballast Water.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Oct 26;16(10):25560-75. doi: 10.3390/ijms161025560. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26516836 Free PMC article.
-
Xurography-based microfluidic algal biosensor and dedicated portable measurement station for online monitoring of urban polluted samples.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Oct 15;117:669-677. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 30007197
-
Effects of sodium hypochlorite treatment on the chlorophyll fluorescence in photosystem II of microalgae.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Aug 10;833:155192. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155192. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35421461
-
Immunoassays in microfluidic systems.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Jun;397(3):991-1007. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3678-8. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20422163 Review.
-
Instrumentation in developing chlorophyll fluorescence biosensing: a review.Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(9):11853-69. doi: 10.3390/s120911853. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23112686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of viability of micro-algae cells by optofluidic hologram pattern.Biomicrofluidics. 2018 Mar 29;12(2):024111. doi: 10.1063/1.5021179. eCollection 2018 Mar. Biomicrofluidics. 2018. PMID: 29657655 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Microalgae System: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Mar 15;27(6):1910. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061910. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Detection of Viability and Concentration of Microalgae Cells Based on Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Bright Field Dual Imaging.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;12(8):896. doi: 10.3390/mi12080896. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34442519 Free PMC article.
-
The Structure, Functions and Potential Medicinal Effects of Chlorophylls Derived from Microalgae.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jan 27;22(2):65. doi: 10.3390/md22020065. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38393036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Microfluidic Device for Classification of Microalgae Cells Based on Simultaneous Analysis of Chlorophyll Fluorescence, Side Light Scattering, Resistance Pulse Sensing.Micromachines (Basel). 2016 Nov 2;7(11):198. doi: 10.3390/mi7110198. Micromachines (Basel). 2016. PMID: 30404370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen A.N., Carlton J.T. Accelerating invasion rate in a highly invaded estuary. Science. 1998;279:555–558. - PubMed
-
- Bij de Vaate A., Jazdzewski K., Ketelaars H.A.M., Gollasch S., van der Velde G. Geographical patterns in range extension of Ponto-Caspian macroinvertebrate species in Europe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002;59:1159–1174.
-
- Drake L.A., Doblin M.A., Dobbs F.C. Potential microbial bioinvasions via ships' ballast water, sediment, and biofilm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007;55:333–341. - PubMed
-
- Boltovskoy D., Almada P., Correa N. Biological invasions: Assessment of threat from ballast-water discharge in Patagonian (Argentina) ports. Environ. Sci. Policy. 2011;14:578–583.
-
- Nadeeshani Nanayakkara K.G., Khorshed Alam A.K.M., Zheng Y.M., Paul Chen J. A low-energy intensive electrochemical system for the eradication of Escherichia coli from ballast water: Process development, disinfection chemistry, and kinetics modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012;64:1238–1245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

