A wireless MEMS-based inclinometer sensor node for structural health monitoring
- PMID: 24287533
- PMCID: PMC3892837
- DOI: 10.3390/s131216090
A wireless MEMS-based inclinometer sensor node for structural health monitoring
Abstract
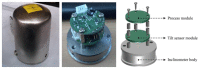
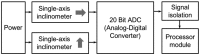
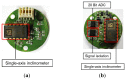
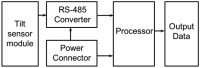
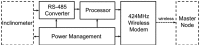
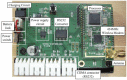
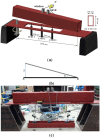
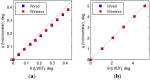
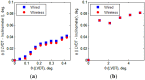
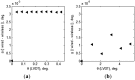
This paper proposes a wireless inclinometer sensor node for structural health monitoring (SHM) that can be applied to civil engineering and building structures subjected to various loadings. The inclinometer used in this study employs a method for calculating the tilt based on the difference between the static acceleration and the acceleration due to gravity, using a micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS)-based accelerometer. A wireless sensor node was developed through which tilt measurement data are wirelessly transmitted to a monitoring server. This node consists of a slave node that uses a short-distance wireless communication system (RF 2.4 GHz) and a master node that uses a long-distance telecommunication system (code division multiple access-CDMA). The communication distance limitation, which is recognized as an important issue in wireless monitoring systems, has been resolved via these two wireless communication components. The reliability of the proposed wireless inclinometer sensor node was verified experimentally by comparing the values measured by the inclinometer and subsequently transferred to the monitoring server via wired and wireless transfer methods to permit a performance evaluation of the wireless communication sensor nodes. The experimental results indicated that the two systems (wired and wireless transfer systems) yielded almost identical values at a tilt angle greater than 1°, and a uniform difference was observed at a tilt angle less than 0.42° (approximately 0.0032° corresponding to 0.76% of the tilt angle, 0.42°) regardless of the tilt size. This result was deemed to be within the allowable range of measurement error in SHM. Thus, the wireless transfer system proposed in this study was experimentally verified for practical application in a structural health monitoring system.
Figures

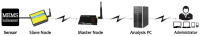


Similar articles
-
A wireless laser displacement sensor node for structural health monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Sep 30;13(10):13204-16. doi: 10.3390/s131013204. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24084114 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a High-Sensitivity Wireless Accelerometer for Structural Health Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jan 17;18(1):262. doi: 10.3390/s18010262. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29342102 Free PMC article.
-
All-IP wireless sensor networks for real-time patient monitoring.J Biomed Inform. 2014 Dec;52:406-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.08.002. Epub 2014 Aug 19. J Biomed Inform. 2014. PMID: 25153310
-
[Advances in sensor node and wireless communication technology of body sensor network].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Jun;29(3):568-73. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22826960 Review. Chinese.
-
A comparative study of wireless sensor networks and their routing protocols.Sensors (Basel). 2010;10(12):10506-23. doi: 10.3390/s101210506. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Sensors (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22163483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Wireless Low-Cost Inclinometer Made from Combining the Measurements of Multiple MEMS Gyroscopes and Accelerometers.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 27;22(15):5605. doi: 10.3390/s22155605. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35957164 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi-Module Fixed Inclinometer for Continuous Monitoring of Landslides: Design, Development, and Laboratory Testing.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 10;20(11):3318. doi: 10.3390/s20113318. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32532152 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Validation of a Scalable, Reconfigurable and Low-Cost Structural Health Monitoring System.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;21(2):648. doi: 10.3390/s21020648. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33477780 Free PMC article.
-
Technique for Determining Bridge Displacement Response Using MEMS Accelerometers.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Feb 19;16(2):257. doi: 10.3390/s16020257. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26907287 Free PMC article.
-
Testing of a MEMS Dynamic Inclinometer Using the Stewart Platform.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 29;19(19):4233. doi: 10.3390/s19194233. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31569499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sohn H., Farrar C.R., Hemez F.M., Shunk D.D., Stinemates D.W., Nadler B.R. A Review of Structural Health Monitoring Literature: 1996–2001. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Los Alamos, NM, USA: 2003.
-
- Chong K.P., Carino N.J., Washer G. Health monitoring of civil infrastructures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2003;12:483–493.
-
- Fan W., Qiao P. Vibration-based damage identification methods: A review and comparative study. Struct. Health Monit. 2011;10:83–111.
-
- Moschas F., Stiros S. Measurement of the dynamic displacements and of the modal frequencies of a short-span pedestrian bridge using GPS and an accelerometer. Eng. Struct. 2011;33:10–17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

