Prolactinoma ErbB receptor expression and targeted therapy for aggressive tumors
- PMID: 24287797
- PMCID: PMC4037394
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-013-0093-x
Prolactinoma ErbB receptor expression and targeted therapy for aggressive tumors
Abstract
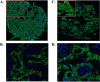
As ErbB signaling is a determinant of prolactin synthesis, role of ErbB receptors was tested for prolactinoma outcomes and therapy. The objective of this study was to characterize ErbB receptor expression in prolactinomas and then perform a pilot study treating resistant prolactinomas with a targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). Retrospective analysis of prolactinomas and pilot study for dopamine agonist resistant prolactinomas in tertiary referral center. We performed immunofluorescent staining of a tissue array of 29 resected prolactinoma tissues for EGFR, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4 correlated with clinical features. Two patients with aggressive resistant prolactinomas enrolled and completed trial. They received lapatinib 1,250 mg daily for 6 months with tumor and hormone assessments. Main outcome measures were positive tumor staining of respective ErbB receptors, therapeutic reduction of prolactin levels and tumor shrinkage. Treated PRL levels and tumor volumes were suppressed in both subjects treated with TKI. EGFR expression was positive in 82 % of adenomas, ErbB2 in 92 %, ErbB3 in 25 %, and ErbB4 in 71 %, with ErbB2 score > EGFR > ErbB4 > ErbB3. Higher ErbB3 expression was associated with optic chiasm compression (p = 0.03), suprasellar extension (p = 0.04), and carotid artery encasement (p = 0.01). Higher DA response rates were observed in tumors with higher ErbB3 expression. Prolactinoma expression of specific ErbB receptors is associated with tumor invasion, symptoms, and response to dopamine agonists. Targeting ErbB receptors may be effective therapy in patients with resistant prolactinomas.
Figures



References
-
- Di Sarno A, Landi ML, Cappabianca P, Di Salle F, Rossi FW, Pivonello R, Di Somma C, Faggiano A, Lombardi G, Colao A. Resistance to cabergoline as compared with bromocriptine in hyperprolactinemia: prevalence, clinical definition, and therapeutic strategy. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2001;86(11):5256–5261. - PubMed
-
- Mancini T, Casanueva FF, Giustina A. Hyperprolactinemia and prolactinomas. Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America. 2008;37(1):67–99. viii. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2007.10.013. - PubMed
-
- Melmed S, Casanueva FF, Hoffman AR, Kleinberg DL, Montori VM, Schlechte JA, Wass JA. Diagnosis and treatment of hyperprolactinemia: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(2):273–288. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1692 96/2/273 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Casanueva FF, Molitch ME, Schlechte JA, Abs R, Bonert V, Bronstein MD, Brue T, Cappabianca P, Colao A, Fahlbusch R, Fideleff H, Hadani M, Kelly P, Kleinberg D, Laws E, Marek J, Scanlon M, Sobrinho LG, Wass JA, Giustina A. Guidelines of the Pituitary Society for the diagnosis and management of prolactinomas. Clinical endocrinology. 2006;65(2):265–273. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02562.x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

