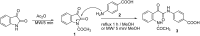OxymaPure/DIC: an efficient reagent for the synthesis of a novel series of 4-[2-(2-acetylaminophenyl)-2-oxo-acetylamino] benzoyl amino acid ester derivatives
- PMID: 24288002
- PMCID: PMC6269765
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules181214747
OxymaPure/DIC: an efficient reagent for the synthesis of a novel series of 4-[2-(2-acetylaminophenyl)-2-oxo-acetylamino] benzoyl amino acid ester derivatives
Abstract
OxymaPure (ethyl 2-cyano-2-(hydroxyimino)acetate) was tested as an additive for use in the carbodiimide (DIC) approach for the synthesis of a novel series of α-ketoamide derivatives (4-[2-(2-acetylaminophenyl)-2-oxo-acetylamino]benzoyl amino acid ester derivatives). OxymaPure showed clear superiority to HOBt/DIC or carbodiimide alone in terms of purity and yield. The title compounds were synthesized via the ring opening of N-acylisatin. First, N-acetylisatin was reacted with 4-aminobenzoic acid under conventional heating as well as microwave irradiation to afford 4-(2-(2-acetamidophenyl)-2-oxoacetamido)benzoic acid. This α-ketoamide was coupled to different amino acid esters using OxymaPure/DIC as a coupling reagent to afford 4-[2-(2-acetylaminophenyl)-2-oxo-acetylamino]benzoyl amino acid ester derivatives in excellent yield and purity. The synthesized compounds were characterized using FT-IR, NMR, and elemental analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Perni R.B., Farmer L.J., Cottrell K.M., Court J.J., Courtney L.F., Deininger D.D., Gates C.A., Harbeson S.L., Kim J.L., Lin C., et al. Inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3·4A protease. Part 3: P2 proline variants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004;14:1939–1942. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.01.078. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources