Ribosomal Database Project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis
- PMID: 24288368
- PMCID: PMC3965039
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1244
Ribosomal Database Project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis
Abstract
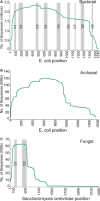
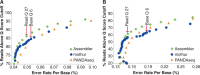
Ribosomal Database Project (RDP; http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) provides the research community with aligned and annotated rRNA gene sequence data, along with tools to allow researchers to analyze their own rRNA gene sequences in the RDP framework. RDP data and tools are utilized in fields as diverse as human health, microbial ecology, environmental microbiology, nucleic acid chemistry, taxonomy and phylogenetics. In addition to aligned and annotated collections of bacterial and archaeal small subunit rRNA genes, RDP now includes a collection of fungal large subunit rRNA genes. RDP tools, including Classifier and Aligner, have been updated to work with this new fungal collection. The use of high-throughput sequencing to characterize environmental microbial populations has exploded in the past several years, and as sequence technologies have improved, the sizes of environmental datasets have increased. With release 11, RDP is providing an expanded set of tools to facilitate analysis of high-throughput data, including both single-stranded and paired-end reads. In addition, most tools are now available as open source packages for download and local use by researchers with high-volume needs or who would like to develop custom analysis pipelines.
Figures

References
-
- Guadet J, Julien J, Lafay JF, Brygoo Y. Phylogeny of some Fusarium species, as determined by large-subunit rRNA sequence comparison. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1989;6:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Schnare MN, Damberger SH, Gray MW, Gutell RR. Comprehensive comparison of structural characteristics in Eukaryotic cytoplasmic large subunit (23S-like) ribosomal RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1996;256:701–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

