Subtoxic Levels of Apigenin Inhibit Expression and Secretion of VEGF by Uveal Melanoma Cells via Suppression of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt Pathways
- PMID: 24288566
- PMCID: PMC3833119
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/817674
Subtoxic Levels of Apigenin Inhibit Expression and Secretion of VEGF by Uveal Melanoma Cells via Suppression of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt Pathways
Abstract
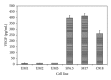
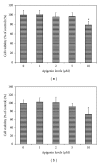
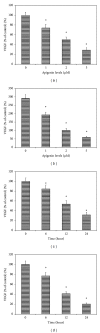
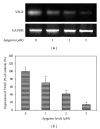
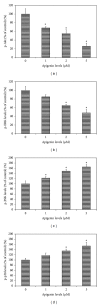
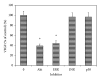
The effects of apigenin on the expression of VEGF in uveal melanoma cells have not been reported. We studied this effect and relevant signaling pathways in two human uveal melanoma cell lines (SP6.5 and C918). ELISA assay revealed that the constitutive secretion of VEGF by uveal melanoma cells was 21-fold higher than that in normal uveal melanocytes. Apigenin at subtoxic levels (1-5 μ M) significantly suppressed the secretion of VEGF in a dose- and time-dependent manner in melanoma cells. VEGF levels in the conditioned culture media from SP6.5 and C918 cell lines treated with 5 μ M apigenin for 24 h reduced to 29% and 21% of those in cells not treated with apigenin, respectively. RT-PCR analysis found that apigenin also decreased the expression of VEGF mRNA in melanoma cells. ELISA study of various signal pathways showed that apigenin significantly decreased phosphorylated Akt and ERK1/2 but increased phosphorylated JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK levels in melanoma cells. PI3K/Akt or ERK1/2 inhibitors significantly decreased, but JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK inhibitors did not influence the secretion of VEGF by melanoma cells, suggesting that apigenin suppresses the secretion of VEGF mainly through the inhibition of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Hu DN, Yu GP, McCormick SA, Schneider S, Finger PT. Population-based incidence of uveal melanoma in various races and ethnic groups. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2005;140(4):612–617. - PubMed
-
- Kujala E, Mäkitie T, Kivelä T. Very long-term prognosis of patients with malignant uveal melanoma. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 2003;44(11):4651–4659. - PubMed
-
- Augsburger JJ, Corrêa ZM, Shaikh AH. Effectiveness of treatments for metastatic uveal melanoma. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2009;148(1):119–127. - PubMed
-
- Xie K, Wei D, Shi Q, Huang S. Constitutive and inducible expression and regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews. 2004;15(5):297–324. - PubMed
-
- Loureiro RMB, D’Amore PA. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in cancer. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews. 2005;16(1):77–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

