Application of genetic algorithm for discovery of core effective formulae in TCM clinical data
- PMID: 24288577
- PMCID: PMC3830796
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/971272
Application of genetic algorithm for discovery of core effective formulae in TCM clinical data
Abstract
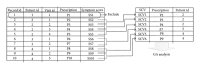
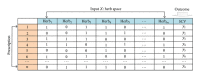
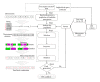
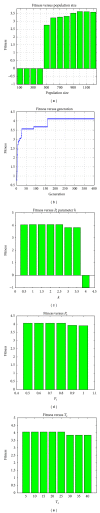
Research on core and effective formulae (CEF) does not only summarize traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment experience, it also helps to reveal the underlying knowledge in the formulation of a TCM prescription. In this paper, CEF discovery from tumor clinical data is discussed. The concepts of confidence, support, and effectiveness of the CEF are defined. Genetic algorithm (GA) is applied to find the CEF from a lung cancer dataset with 595 records from 161 patients. The results had 9 CEF with positive fitness values with 15 distinct herbs. The CEF have all had relative high average confidence and support. A herb-herb network was constructed and it shows that all the herbs in CEF are core herbs. The dataset was divided into CEF group and non-CEF group. The effective proportions of former group are significantly greater than those of latter group. A Synergy index (SI) was defined to evaluate the interaction between two herbs. There were 4 pairs of herbs with high SI values to indicate the synergy between the herbs. All the results agreed with the TCM theory, which demonstrates the feasibility of our approach.
Figures
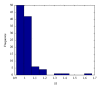
Similar articles
-
A Semantic Analysis and Community Detection-Based Artificial Intelligence Model for Core Herb Discovery from the Literature: Taking Chronic Glomerulonephritis Treatment as a Case Study.Comput Math Methods Med. 2020 Sep 1;2020:1862168. doi: 10.1155/2020/1862168. eCollection 2020. Comput Math Methods Med. 2020. PMID: 32952598 Free PMC article.
-
[Effective core formulae for lung cancer based on complex network and survival analysis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Nov;40(22):4482-90. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 27097428 Chinese.
-
Herb network construction and co-module analysis for uncovering the combination rule of traditional Chinese herbal formulae.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Dec 14;11 Suppl 11(Suppl 11):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-S11-S6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21172056 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine formulas for the treatment of osteoporosis: Implication for antiosteoporotic drug discovery.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:61-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.025. Epub 2016 May 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27180315 Review.
-
Herb pairs containing Angelicae Sinensis Radix (Danggui): A review of bio-active constituents and compatibility effects.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 2;181:158-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.033. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26807913 Review.
Cited by
-
The Common Prescription Patterns Based on the Hierarchical Clustering of Herb-Pairs Efficacies.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:6373270. doi: 10.1155/2016/6373270. Epub 2016 Apr 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27190534 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Patient Classification for Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Machine Learning Perspective.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:376716. doi: 10.1155/2015/376716. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26246834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ingredients, Anti-Liver Cancer Effects and the Possible Mechanism of DWYG Formula Based on Network Prediction.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 15;13:4213-4227. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S238901. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32523357 Free PMC article.
-
TCMNPAS: a comprehensive analysis platform integrating network formulaology and network pharmacology for exploring traditional Chinese medicine.Chin Med. 2024 Mar 22;19(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00924-y. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38519956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and possible mechanism of Ruyiping formula application to breast cancer based on network prediction.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 27;9(1):5249. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41243-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30918282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes PM, Bloom B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. National Health Statistics Reports. 2009;(12):1–23. - PubMed
-
- Lan H, Lu Y, Jin K, Zhu T, Jin Z. Data mining: a modern tool to investigate Traditional Chinese Medicine. Journal of US-China Medical Science. 2011;8(5):316–320.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

