Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in chronic epicondylitis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24289799
- PMCID: PMC4220815
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-410
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in chronic epicondylitis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Tendinopathy is a difficult problem to manage and can result in significant patient morbidity. Currently, the clinical use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in painful tendons is widespread but its efficacy remains controversial.
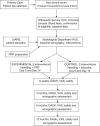
Methods/design: This study is a single-center, randomized double-blind controlled trial. Eighty patients will be allocated to have ultrasound (US)-guided needling combined with a leukocyte-depleted (that is, pure) PRP or lidocaine each alternate week for a total of two interventions. Outcome data will be collected before intervention, and at 6 weeks, 3, 6, and 12 months after intervention.
Main outcome measure: Changes in pain and activity levels, as assessed by Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH-E, Spanish version) score, at 6 months. We will compare the percentage of patients in each group that achieve a successful treatment defined as a reduction of at least 25% in the DASH-E score. Secondary outcome measures include changes in DASH-E at 3 and 12 months, changes in pain as assessed by the visual analogue scale (VAS) at the 6-week, 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-up, changes in sonographic features and neovascularity, and percentage of patients in each group with adverse reactions at 3, 6, and 12 months.
Discussion: The results of this study will provide insights into the effect of pure PRP in tendon and may contribute to identifying the best protocol for PRP application in tendinopathies.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01945528.
References
-
- Andia I, Abate M. Platelet rich plasma injections for tendinopathy and osteoarthritis. Int J Clin Rheumatol. 2012;7:397–412. doi: 10.2217/ijr.12.36. - DOI
-
- Creaney L, Walla A, Curtis M, Connell D. Growth factor-based therapies provide additional benefit beyond physical therapy in resistant elbow tendinopathy: a prospective, double-blind, randomised trial of autologous blood injections versus platelet-rich plasma injections. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45:966–971. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2010.082503. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krogh TP, Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Christensen R, Jensen P, Ellingsen T. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:625–635. doi: 10.1177/0363546512472975. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials