Whole-exome sequencing of 2,000 Danish individuals and the role of rare coding variants in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 24290377
- PMCID: PMC3852935
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.11.005
Whole-exome sequencing of 2,000 Danish individuals and the role of rare coding variants in type 2 diabetes
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2014 Mar 6;94(3):479
Abstract
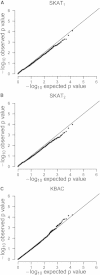
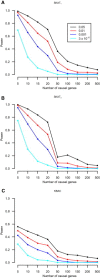
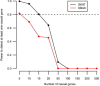
It has been hypothesized that, in aggregate, rare variants in coding regions of genes explain a substantial fraction of the heritability of common diseases. We sequenced the exomes of 1,000 Danish cases with common forms of type 2 diabetes (including body mass index > 27.5 kg/m(2) and hypertension) and 1,000 healthy controls to an average depth of 56×. Our simulations suggest that our study had the statistical power to detect at least one causal gene (a gene containing causal mutations) if the heritability of these common diseases was explained by rare variants in the coding regions of a limited number of genes. We applied a series of gene-based tests to detect such susceptibility genes. However, no gene showed a significant association with disease risk after we corrected for the number of genes analyzed. Thus, we could reject a model for the genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes where rare nonsynonymous variants clustered in a modest number of genes (fewer than 20) are responsible for the majority of disease risk.
Copyright © 2013 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Contribution of Low-Frequency and Rare Coding Variation to Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Apr 8;19(5):25. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1142-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 30957210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare coding variants in 35 genes associate with circulating lipid levels-A multi-ancestry analysis of 170,000 exomes.Am J Hum Genet. 2022 Jan 6;109(1):81-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.11.021. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 34932938 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing of Danish Holstein dairy cattle for variant detection and insight into potential loss-of-function variants in protein coding genes.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 9;16:1043. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2249-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26645365 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and functional impact of rare coding variation from deep sequencing of human exomes.Science. 2012 Jul 6;337(6090):64-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1219240. Epub 2012 May 17. Science. 2012. PMID: 22604720 Free PMC article.
-
What will diabetes genomes tell us?Curr Diab Rep. 2012 Dec;12(6):643-50. doi: 10.1007/s11892-012-0321-4. Curr Diab Rep. 2012. PMID: 22983892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Contribution of Low-Frequency and Rare Coding Variation to Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Apr 8;19(5):25. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1142-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 30957210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from exome sequencing for endocrine disorders.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 Aug;11(8):455-64. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.72. Epub 2015 May 12. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25963271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes in Population Isolates: Lessons from Greenland.Rev Diabet Stud. 2015 Fall-Winter;12(3-4):320-9. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2015.12.320. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Rev Diabet Stud. 2015. PMID: 27111118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Novel Candidate Markers of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity in Russia by Exome Sequencing with a Limited Sample Size.Genes (Basel). 2018 Aug 17;9(8):415. doi: 10.3390/genes9080415. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30126146 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted next generation sequencing in a young population with suspected inherited malignant cardiac arrhythmias.Eur J Hum Genet. 2018 Mar;26(3):303-313. doi: 10.1038/s41431-017-0060-8. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Eur J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29343803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King R.A., Rotter J.I., Motulsky A.G. Oxford University Press; New York, NY: 2002. The Genetic Basis of Common Diseases.
-
- Risch N.J. Searching for genetic determinants in the new millennium. Nature. 2000;405:847–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

