Bioengineering radioresistance by overproduction of RPA, a mammalian-type single-stranded DNA-binding protein, in a halophilic archaeon
- PMID: 24292079
- PMCID: PMC4096848
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-013-5368-x
Bioengineering radioresistance by overproduction of RPA, a mammalian-type single-stranded DNA-binding protein, in a halophilic archaeon
Abstract
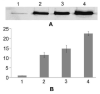
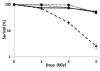
Halobacterium sp. NRC-1 is a wild-type extremophilic microbe that is naturally tolerant to high levels of ionizing radiation. Mutants of strain NRC-1 with even higher levels of resistance to ionizing radiation, named RAD, were previously isolated after selecting survival to extremely high doses of ionizing radiation. These RAD mutants displayed higher transcription levels for the rfa3 operon, coding two subunits of the RPA-like putative single-stranded binding protein, rfa3 and rfa8, and a third downstream gene, ral. In order to bioengineer cells with increased tolerance to ionizing radiation and further explore the genetic basis of the RAD phenotype, we placed the rfa3 operon under control of the gvpA promoter in a Halobacterium expression plasmid, pDRK1. When pDRK1 was introduced into the wild-type NRC-1 strain, overproduction of the Rfa3 and Rfa8 proteins was observed by Western blotting and proteomic analysis. The Halobacterium strains expressing Rfa3 and Rfa8 also displayed improved survival after exposure to ionizing radiation, similar to the RAD mutants, when compared to wild-type strain NRC-1. The Rfa3 and Rfa8 proteins co-purified by affinity chromatography on single-stranded DNA cellulose columns, confirming the ability of the proteins to bind to single-stranded DNA as well as their relative abundance in the wild-type, RAD mutants, and rfa3 operon overexpression strains. These results clearly establish that overexpression of haloarchaeal RPA promotes ionizing radiation resistance in Halobacterium sp. NRC-1 and that the Rfa3 and Rfa8 subunits bind single-stranded DNA. Bioengineering cells with increased levels of ionizing radiation resistance may have potential value in medical and environmental applications.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extremely radiation-resistant mutants of a halophilic archaeon with increased single-stranded DNA-binding protein (RPA) gene expression.Radiat Res. 2007 Oct;168(4):507-14. doi: 10.1667/RR0935.1. Radiat Res. 2007. PMID: 17903038
-
An improved genetic system for bioengineering buoyant gas vesicle nanoparticles from Haloarchaea.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Dec 21;13:112. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-112. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24359319 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of an extreme halophilic archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2003 Aug;2(8):506-24. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M300044-MCP200. Epub 2003 Jul 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2003. PMID: 12872007
-
Protein transport in the halophilic archaeon Halobacterium sp. NRC-1: a major role for the twin-arginine translocation pathway?Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Nov;148(Pt 11):3335-3346. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-11-3335. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12427925 Review. No abstract available.
-
Regulation of gas vesicle formation in halophilic archaea.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 May;4(3):175-81. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11931543 Review.
Cited by
-
Haloarchaeal gas vesicle nanoparticles displaying Salmonella SopB antigen reduce bacterial burden when administered with live attenuated bacteria.Vaccine. 2014 Jul 31;32(35):4543-4549. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.021. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24950351 Free PMC article.
-
Bioengineering novel floating nanoparticles for protein and drug delivery.Mater Today Proc. 2016;3(2):206-210. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2016.01.058. Mater Today Proc. 2016. PMID: 27158595 Free PMC article.
-
An Antarctic Extreme Halophile and Its Polyextremophilic Enzyme: Effects of Perchlorate Salts.Astrobiology. 2018 Apr;18(4):412-418. doi: 10.1089/ast.2017.1766. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Astrobiology. 2018. PMID: 29189043 Free PMC article.
-
The archaeal class Halobacteria and astrobiology: Knowledge gaps and research opportunities.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1023625. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1023625. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36312929 Free PMC article.
-
Haloarchaeal gas vesicle nanoparticles displaying Salmonella antigens as a novel approach to vaccine development.Procedia Vaccinol. 2015;9:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.provac.2015.05.003. Procedia Vaccinol. 2015. PMID: 26900411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berquist BR, Müller JA, DasSarma S. Methods in microbiology. In: Oren A, Rainey F, editors. Genetic systems for halophilic archaea. Volume 35. Elsevier/Academic Press; London: 2006. pp. 649–680.
-
- Capes MD, Coker JA, Gessler R, Grinblat-Huse V, DasSarma SL, Jacob CG, Kim JM, DasSarma P, DasSarma S. The information transfer system of halophilic archaea. Plasmid. 2011;65:77–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

