Intensity-modulated and hypofractionated simultaneous integrated boost adjuvant breast radiation employing statics ports of tomotherapy (TomoDirect): a prospective phase II trial
- PMID: 24292425
- PMCID: PMC11823710
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-013-1560-8
Intensity-modulated and hypofractionated simultaneous integrated boost adjuvant breast radiation employing statics ports of tomotherapy (TomoDirect): a prospective phase II trial
Abstract
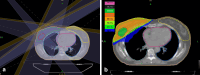
Purpose: To report the 1-year outcomes of a prospective phase II study on hypofractionated whole-breast intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IM-WBRT) with a simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) to the tumor bed delivered with static ports of tomotherapy (TomoDirect) (TD).
Methods: A prospective cohort of 82 patients was enrolled between 2011 and 2012. Treatment schedule consisted of 45 Gy/20 fractions to the whole breast and 50 Gy/20 fractions to the surgical bed delivered concomitantly with TD over 4 weeks. A one-armed optimal two-stage Simon's design was selected to test the hypothesis that treatment modality under investigation would decrease acute skin toxicity over historical data using conventional fractionation and sequential boost. Primary endpoint was acute skin toxicity. Secondary endpoints included late toxicity, cosmesis, quality of life and local control.
Results: Median follow-up was 12 months (range 6-18). Maximum detected acute skin toxicity was G0 41 %; G1 53 %; G2 6 %; G3 <1 %. With two G2-G3 acute skin toxicity events in the first stage and four in the second, the study fulfilled the requirements for the definition of the treatment approach under investigation as promising. Late skin toxicity was mild with no >G2 events. Cosmesis was good/excellent in 91 % of patients and fair/poor in 9 %. Quality of life was preserved over time, with the exception of fatigue, which was transiently increased.
Conclusions: Hypofractionated IM-WBRT with a SIB to the tumor bed delivered with TD provides consistent clinical results and it is able to reduce acute skin toxicity rate over conventionally fractionated and sequential boost tomotherapy-based IM-WBRT.
Figures
References
-
- Bantema-Joppe EJ, Schilstra C, de Bock GH, Dolsma WV, Busz DM, Langendijk JA, Maduro JH (2012) Simultaneous integrated boost irradiation after breast conserving surgery: physician-rated toxicity and cosmetic outcome at 30 months’ follow up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(4):e471–e477 - PubMed
-
- Barnett GC, Wilkinson JS, Moody A, Wilson CB, Twyman N, Wishart GC, Burnet NG, Coles CE (2012) Randomized controlled trial of forward-planned intensity modulated-radiotherapy for early breast cancer: interim results at 2 years. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(2):715–723 - PubMed
-
- Bartelink H, Horiot JC, Poortmans PM, Struikmans H, Van den Bogaert W, Fourquet A, Jager JJ, Hoogenraad WJ, Oei SB, Warlam-Rodenhuis CC, Pierart M, Colette L (2007) Impact of a higher radiation dose on local control and survival in breast-conserving therapy of early breast cancer: 10 years results of the randomized boost versus no boost EORTC 22881-10882 trial. J Clin Oncol 25(22):3259–3265 - PubMed
-
- Borca VC, Franco P, Catuzzo P, Migliaccio F, Zenone F, Aimonetto S, Peruzzo A, Pasquino M, Russo G, La Porta MR, Cante D, Sciacero P, Girelli G, Ricardi U, Tofani S (2012) Does TomoDirect 3DCRT represent a suitable option for post-operative whole breast irradiation? A hypothesis-generating pilot study. Radiat Oncol 7:211 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cante D, Rosa La Porta M, Casanova-Borca V, Sciacero P, Girelli G, Pasquino M, Franco P, Ozzello F (2011) Accelerated hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast radiotherapy with concomitant photon boost after conserving surgery for early breast cancer: a prospective evaluation on 463 patients. Breast J 17(6):586–593 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical