Drosophila life span and physiology are modulated by sexual perception and reward
- PMID: 24292624
- PMCID: PMC4042187
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1243339
Drosophila life span and physiology are modulated by sexual perception and reward
Abstract
Sensory perception can modulate aging and physiology across taxa. We found that perception of female sexual pheromones through a specific gustatory receptor expressed in a subset of foreleg neurons in male fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster, rapidly and reversibly decreases fat stores, reduces resistance to starvation, and limits life span. Neurons that express the reward-mediating neuropeptide F are also required for pheromone effects. High-throughput whole-genome RNA sequencing experiments revealed a set of molecular processes that were affected by the activity of the longevity circuit, thereby identifying new candidate cell-nonautonomous aging mechanisms. Mating reversed the effects of pheromone perception; therefore, life span may be modulated through the integrated action of sensory and reward circuits, and healthy aging may be compromised when the expectations defined by sensory perception are discordant with ensuing experience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
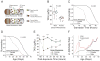
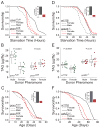
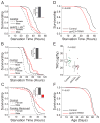
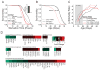
Comment in
-
Development. Chemical warfare in the battle of the sexes.Science. 2014 Jan 31;343(6170):491-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1250174. Science. 2014. PMID: 24482469 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32GM008322/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030593/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32AG042253/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- TR01AG043972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG-013283/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG023166/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000114/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM102279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32AG000114/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AG042253/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG030593/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008322/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023166/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013283/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

