Energetic analysis of the rhodopsin-G-protein complex links the α5 helix to GDP release
- PMID: 24292645
- PMCID: PMC3947367
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2705
Energetic analysis of the rhodopsin-G-protein complex links the α5 helix to GDP release
Abstract
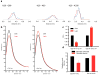
We present a model of interaction of Gi protein with the activated receptor (R*) rhodopsin, which pinpoints energetic contributions to activation and reconciles the β2 adrenergic receptor-Gs crystal structure with new and previously published experimental data. In silico analysis demonstrated energetic changes when the Gα C-terminal helix (α5) interacts with the R* cytoplasmic pocket, thus leading to displacement of the helical domain and GDP release. The model features a less dramatic domain opening compared with the crystal structure. The α5 helix undergoes a 63° rotation, accompanied by a 5.7-Å translation, that reorganizes interfaces between α5 and α1 helices and between α5 and β6-α5. Changes in the β6-α5 loop displace αG. All of these movements lead to opening of the GDP-binding pocket. The model creates a roadmap for experimental studies of receptor-mediated G-protein activation.
Figures
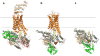




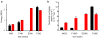
References
-
- Onrust R, et al. Receptor and βγ Binding Sites in the α Subunit of the Retinal G Protein Transducin. Science. 1997;275:381–384. - PubMed
-
- Mazzoni MR, Hamm HE. Interaction of Transducin with Light-activated Rhodopsin Protects It from Proteolytic Digestion by Trypsin. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:30034–30040. - PubMed
-
- Slessareva JE, et al. Closely Related G-protein-coupled Receptors Use Multiple and Distinct Domains on G-protein α-Subunits for Selective Coupling. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278:50530–50536. - PubMed
-
- Marin EP, Krishna AG, Sakmar TP. Disruption of the alpha5 helix of transducin impairs rhodopsin-catalyzed nucleotide exchange. Biochemistry. 2002;41:6988–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 MH086222/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097376/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM080403/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH086222/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027091/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM084757/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 GM084757/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090192/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY006062/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM099842/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008320/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM087519/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY006062/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

