The fixed-dose combination of olmesartan/amlodipine was superior in central aortic blood pressure reduction compared with perindopril/amlodipine: a randomized, double-blind trial in patients with hypertension
- PMID: 24293132
- PMCID: PMC3898428
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-013-0076-6
The fixed-dose combination of olmesartan/amlodipine was superior in central aortic blood pressure reduction compared with perindopril/amlodipine: a randomized, double-blind trial in patients with hypertension
Erratum in
- Adv Ther. 2014 Apr;31(4):472
- Adv Ther. 2014 Feb;31(2):243
-
Erratum to: The fixed-dose combination of olmesartan/amlodipine was superior in central aortic blood pressure reduction compared with perindopril/amlodipine: a randomized, double-blind trial in patients with hypertension.Adv Ther. 2015 Feb;32(2):184-5. doi: 10.1007/s12325-015-0186-4. Adv Ther. 2015. PMID: 25712918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Central blood pressure (BP), an important measure of cardiovascular risk, has been shown to be effectively reduced by calcium channel blockade with amlodipine (AML) plus renin-angiotensin system blockade by the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, perindopril (PER). The aim of the SEVITENSION study was to compare the central effects of PER/AML against renin-angiotensin system blockade with the angiotensin II receptor blocker olmesartan (OLM) plus AML.
Methods: In this multicenter, parallel group, non-inferiority study, patients received AML 10 mg during a 2- to 4-week run-in before randomization to 24 weeks of double-blind treatment with the fixed-dose combination of OLM/AML 40/10 mg or PER/AML 8/10 mg. Hydrochlorothiazide was added at Weeks 4, 8, or 12 in patients with inadequate BP control. The primary efficacy variable was the absolute change in central systolic BP (CSBP) from baseline to the final examination, measured by radial artery applanation tonometry and analyzed by parametric analysis of covariance. Secondary variables included 24-h ambulatory and seated BP measurements as well as BP normalization.
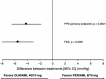
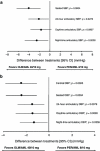
Results: Of 600 patients enrolled, 486 were randomized (244 to OLM/AML 40/10 mg, 242 to PER/AML 8/10 mg). The reduction in CSBP was larger with OLM/AML (14.5 ± 0.83 mmHg) than with PER/AML (10.4 ± 0.84 mmHg). The between-group difference was -4.2 ± 1.18 mmHg with 95% confidence intervals (-6.48 to -1.83 mmHg) within the predefined non-inferiority margin (2 mmHg). An integrated superiority test confirmed that OLM/AML was superior to PER/AML (p < 0.0001) in reducing CSBP. The superiority of OLM/AML over PER/AML was also established for the majority of secondary efficacy variables; at the final examination, 75.6% of OLM/AML recipients achieved BP normalization (mean seated systolic BP/diastolic BP <140/90 mmHg) compared with 57.5% of PER/AML recipients (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: The combination of OLM/AML was superior to PER/AML in reducing CSBP and other efficacy measures, including a significantly higher rate of BP normalization.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01101009.
Figures



Comment in
-
Additional information regarding the SEVITENSION study.Adv Ther. 2014 Aug;31(8):777-9. doi: 10.1007/s12325-014-0144-6. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Adv Ther. 2014. PMID: 25145548 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Fixed-Combination Olmesartan/Amlodipine Was Superior to Perindopril + Amlodipine in Reducing Central Systolic Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Patients With Diabetes.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016 Jun;18(6):528-35. doi: 10.1111/jch.12673. Epub 2015 Sep 23. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016. PMID: 26395174 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Study of the Efficacy of Olmesartan/Amlodipine vs. Perindopril/Amlodipine in Peripheral and Central Blood Pressure Parameters After Missed Dose in Type 2 Diabetes.Am J Hypertens. 2016 Sep;29(9):1055-62. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpw033. Epub 2016 May 24. Am J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27220840 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of triple antihypertensive therapy with the olmesartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide combination.Clin Drug Investig. 2012 Oct 1;32(10):649-64. doi: 10.1007/BF03261919. Clin Drug Investig. 2012. PMID: 22909147 Clinical Trial.
-
Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil or valsartan in combination with amlodipine: a review of factorial-design studies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Jan;25(1):177-85. doi: 10.1185/03007990802597456. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19210150 Review.
-
Blood pressure control with angiotensin receptor blocker-based three-drug combinations: key trials.Adv Ther. 2012 May;29(5):401-15. doi: 10.1007/s12325-012-0019-7. Epub 2012 May 17. Adv Ther. 2012. PMID: 22610686 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Amlodipine/Valsartan Versus Nebivolol/Valsartan Fixed Dose Combinations on Peripheral and Central Blood Pressure.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2018 Dec;25(4):407-413. doi: 10.1007/s40292-018-0286-8. Epub 2018 Nov 3. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2018. PMID: 30390203 Clinical Trial.
-
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Versus Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors for the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension and the Role of Olmesartan.Adv Ther. 2019 Feb;36(2):278-297. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0859-x. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 30591990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Hypertension Using Olmesartan Alone or in Combination.Cardiol Ther. 2017 Jun;6(1):13-32. doi: 10.1007/s40119-017-0087-5. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Cardiol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28258390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central blood pressure for the management of hypertension: Is it a practical clinical tool in current practice?J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020 Mar;22(3):391-406. doi: 10.1111/jch.13758. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020. PMID: 31841279 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Central Blood Pressure Monitoring in the Management of Hypertension.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018 Apr 19;20(6):41. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-0991-x. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29675613 Review.
References
-
- Williams B, Lacy PS, Thom SM, et al. Differential impact of blood pressure-lowering drugs on central aortic pressure and clinical outcomes: principal results of the Conduit Artery Function Evaluation (CAFE) study. Circulation. 2006;113:1213–1225. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.606962. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dahlof B, Sever PS, Poulter NR, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366:895–906. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67185-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2159–2219. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht151. - DOI - PubMed
-
- ONTARGET Investigators, Yusuf S, Teo KK, et al. Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1547–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

